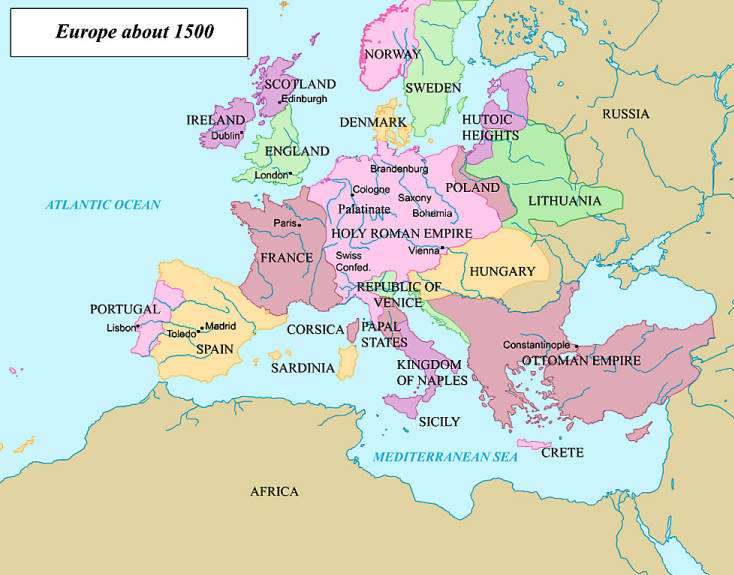
George Frideric Handel was a law school drop out, last chair violinist¹, and the first international composing superstar. Born in what is now Halle Germany, Handel overcame parental disapproval, explosive duels, and a rigid patronage system to become one of the most famous composers of all time.
Handel was born in 1685 in Halle, then a part of the Holy Roman Empire. His father, Georg Handel, was a barber surgeon, and wanted his son to have an equally dignified profession. He forbade young George from pursuing his musical interests. His reasoning was the same as that of many parents of budding musicians--there was no financially stable career in music. Luckily Handel's mother, Dorthea, was of a different opinion. She encouraged her son to explore music, helping him hide a clavichord in the attic. Young Handel spent many hours practicing in secret.²
In 1702 Handel headed to the city of Trier to begin law school. However, he spent much more time studying organ with Friedrich Wilhelm Zachow³, and eventually dropped out of law school to pursue music full time. It seemed likely that Handel would become the next cathedral organist, but in 1703 he quit, and took a job in Hamburg as a violinist with the Goose Market Theatre.
While in Hamburg Handel taught private music lessons to supplement his income, took over some Harpsichordist duties with the orchestra, and composed furiously. 1705 saw the premier of his first opera, Almira, just three years after his arrival in Hamburg.
Also notable during his Hamburg years, Handel fought a duel with his friend Johann Mattheson. Mattheson, a composer, singer, and conductor was performing as Antony in his opera Cleopatra. After his death in act three of the opera Mattheson decided to take over as conductor of the orchestra. This was, as composer of the work, his right. Like most conductors of the day, Mattheson conducted from the harpsichord. However, when he reached the harpsichord to relieve George Handel, Handel refused to budge. This resolved into a bitter argument during the opera, which culminated in the men taking the fight outside, swords drawn. Mattheson nearly killed Handel that night, but Handel was, quite luckily, saved by a coat button. The two men resolved their quarrel soon after the duel, and remained friends until the end of their lives.
In 1706 Handel left Hamburg for Italy. He traveled around the Italian peninsula, hobnobbing with notable instrumental and opera composers of the day--Corelli, Lully, and both Domenico and Alessandro Scarlatti. During his years in Italy, Handel developed a taste for opera, and begin writing his own operas in a more Italian style. He composed two major operas in Italy--Rodrigo and Agrippina. Both premiered in Italy, and made Handel a household name in the Italian opera scene. In under four years, Handel went from virtually unknown to a rising superstar.
Handel was well known enough that he was offered the position as Kapellmeister to the Elector of Hanover. However, Handel's stay in Hanover was brief. By 1711 he had set out for London--the city he would call home for most of the rest of his life.
1711 saw Handel's opera Rinaldo premiere, which was an instant hit. It was the first Italian Opera written specifically for London, it contained dazzling effects, and featured stirring arias sung by experts. Rinaldo ran for a whopping 47 performances--an enormously long run for the time.
Following Rinaldo Handel produced hit after hit after hit. His work was so popular that in 1712 he received an annual salary of 200 pounds from Queen Anne, about 33,000 pounds in 2018 currency. He desperately wanted to stay in London--a city that eagerly embraced his work--and in 1714 London became his permanent home after his boss, the Elector of Hanover, became King George I of England.
However, in 1728 Italian opera started to go out of vogue. Attendance fell, and operas still had to deal with enormous production costs, making it difficult for companies to remain in the black. In addition to financial troubles, Handel and his colleagues had to deal with the perceived immorality of opera, and disapproval of the pious English public. Beneath all this, it is unsurprising that in 1737, Handel's opera company folded.
Handel then turned his attention to oratorios. Oratorios had the advantage of telling a grandiose story in song, but didn't have the high production cost of an opera. Additionally, since they weren't being presented in a play (the height of immorality), oratorios could safely tell religious stories. It was with these religious works that Handel really made his mark.
The first proto-oratorio was a revival of one of Handel's previous works, Esther. Esther was a wide departure from opera, featuring English lyrics, and no acting whatsoever. It was received well, and in 1733 Handel launched his first full oratorio Deborah and Athalia.
Though Handel did continue to write operas until 1741, he mainly produced oratorios from 1733 until the end of his life. He composed a total of 29 oratorios, with the most famous being his Messiah.
Handel died in 1759 at the age of 74. There was a staggering amount of public grief at his passing, and more than 3,000 people attended his funeral from all over Europe. A commemorative concert was put on 25 years after his death, and his works have remained constantly in performance ever since. Though he was born in Germany, England so thoroughly adopted him that he was laid to rest in Poet's Corner in Westminster Abbey.
¹Although in Handel's time seats within the orchestra weren't referred to as chairs, they were called desks.
²For those wondering how Georg Handel didn't notice a clavichord being played in his own home, it is worth noting that the clavichord is a notoriously quiet instrument, part of why it was later replaced by the piano in the modern orchestra.
³For those wondering how Papa Handel responded, Papa Handel unfortunately died in 1696.
Sources
The Lives of the Great Composers by Harold C. Schonberg
Eric W. Nye, Pounds Sterling to Dollars: Historical Conversion of Currency, accessed Saturday, December 15, 2018, http://www.uwyo.edu/numimage/currency.htm.
George Frideric Handel (1685-1759)
George Frideric Handel. German-English Composer
Duel with Mattheson
A Biographical Introduction
George Frideric Handel-Composer
George Frideric Handel, and His Life Saving Coat Button
 |
| Handel himself. |
In 1702 Handel headed to the city of Trier to begin law school. However, he spent much more time studying organ with Friedrich Wilhelm Zachow³, and eventually dropped out of law school to pursue music full time. It seemed likely that Handel would become the next cathedral organist, but in 1703 he quit, and took a job in Hamburg as a violinist with the Goose Market Theatre.
While in Hamburg Handel taught private music lessons to supplement his income, took over some Harpsichordist duties with the orchestra, and composed furiously. 1705 saw the premier of his first opera, Almira, just three years after his arrival in Hamburg.
Also notable during his Hamburg years, Handel fought a duel with his friend Johann Mattheson. Mattheson, a composer, singer, and conductor was performing as Antony in his opera Cleopatra. After his death in act three of the opera Mattheson decided to take over as conductor of the orchestra. This was, as composer of the work, his right. Like most conductors of the day, Mattheson conducted from the harpsichord. However, when he reached the harpsichord to relieve George Handel, Handel refused to budge. This resolved into a bitter argument during the opera, which culminated in the men taking the fight outside, swords drawn. Mattheson nearly killed Handel that night, but Handel was, quite luckily, saved by a coat button. The two men resolved their quarrel soon after the duel, and remained friends until the end of their lives.
 |
| Program for Handel's opera Rodrigo |
Handel was well known enough that he was offered the position as Kapellmeister to the Elector of Hanover. However, Handel's stay in Hanover was brief. By 1711 he had set out for London--the city he would call home for most of the rest of his life.
1711 saw Handel's opera Rinaldo premiere, which was an instant hit. It was the first Italian Opera written specifically for London, it contained dazzling effects, and featured stirring arias sung by experts. Rinaldo ran for a whopping 47 performances--an enormously long run for the time.
Following Rinaldo Handel produced hit after hit after hit. His work was so popular that in 1712 he received an annual salary of 200 pounds from Queen Anne, about 33,000 pounds in 2018 currency. He desperately wanted to stay in London--a city that eagerly embraced his work--and in 1714 London became his permanent home after his boss, the Elector of Hanover, became King George I of England.
However, in 1728 Italian opera started to go out of vogue. Attendance fell, and operas still had to deal with enormous production costs, making it difficult for companies to remain in the black. In addition to financial troubles, Handel and his colleagues had to deal with the perceived immorality of opera, and disapproval of the pious English public. Beneath all this, it is unsurprising that in 1737, Handel's opera company folded.
Handel then turned his attention to oratorios. Oratorios had the advantage of telling a grandiose story in song, but didn't have the high production cost of an opera. Additionally, since they weren't being presented in a play (the height of immorality), oratorios could safely tell religious stories. It was with these religious works that Handel really made his mark.
The first proto-oratorio was a revival of one of Handel's previous works, Esther. Esther was a wide departure from opera, featuring English lyrics, and no acting whatsoever. It was received well, and in 1733 Handel launched his first full oratorio Deborah and Athalia.
 |
| Handel's house is preserved as a museum in London. |
Handel died in 1759 at the age of 74. There was a staggering amount of public grief at his passing, and more than 3,000 people attended his funeral from all over Europe. A commemorative concert was put on 25 years after his death, and his works have remained constantly in performance ever since. Though he was born in Germany, England so thoroughly adopted him that he was laid to rest in Poet's Corner in Westminster Abbey.
¹Although in Handel's time seats within the orchestra weren't referred to as chairs, they were called desks.
²For those wondering how Georg Handel didn't notice a clavichord being played in his own home, it is worth noting that the clavichord is a notoriously quiet instrument, part of why it was later replaced by the piano in the modern orchestra.
³For those wondering how Papa Handel responded, Papa Handel unfortunately died in 1696.
Sources
The Lives of the Great Composers by Harold C. Schonberg
Eric W. Nye, Pounds Sterling to Dollars: Historical Conversion of Currency, accessed Saturday, December 15, 2018, http://www.uwyo.edu/numimage/currency.htm.
George Frideric Handel (1685-1759)
George Frideric Handel. German-English Composer
Duel with Mattheson
A Biographical Introduction
George Frideric Handel-Composer
George Frideric Handel, and His Life Saving Coat Button