Before beginning, it is important to note that there is not a lot written about Mara in English. Most of the scholarship done about her is written in Serbian, and as The Nerd is not familiar with Serbian, translation apps were used to translate web pages and documents. The Nerd apologizes in advance for any mistakes or misrepresentations which may have occurred because of translation errors.
As far as obscure Slavic princesses go, Mara Branković, eldest daughter of the Serbian Despot¹, Đurađ Branković, is pretty obscure. She has been all but forgotten to the world, yet for several decades she was one of the most important diplomats in Europe, helping to keep a tenuous peace between the Muslim Ottomans, and the Christian everybody else.
Mara was the daughter of Đurađ Branković and his second wife, Irene. Maybe. She may have been the daughter of Đurađ's first, unnamed wife. The documentation is shaky, and it's difficult to know exactly when and to whom Mara was born. What is for sure is that she was the second of five children--two girls and three boys.
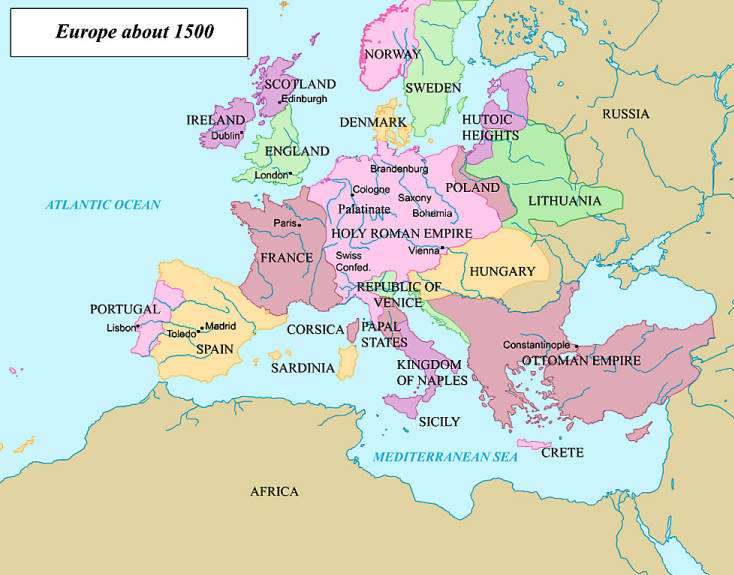
Serbia, at the time, was in a shaky spot. Sandwiched between the rapidly growing Ottoman Empire, and the land hungry Hungarian Empire, Serbia was put in the precarious position of having to serve two masters who didn't like each other. Đurađ had been able to gain the position of despot by only the skin of his teeth, after the previous despot died without an heir. he required the approval of the leaders of his powerful neighbors to retain his position. In order to appease the pair, he gave his daughters to them in marriage, Mara to Sultan Murad II, and her sister, Katrina, to the Count of Hungary.
Mara was 21 at the age of her marriage in 1433. The sultan was fifteen years older than her, and already had a wife and an heir. Murad supposedly wasn't initially too keen on marrying the daughter of his lowly client king, but when her father offered most of Serbia as a dowry, Murad seized on the opportunity.
The years of Mara's marriage were fairly quiet. Murad favored Mara, but reportedly never consummated the relationship. Mara got on well with Murad's other wife, and his son. She served as an intermediary between her father and her husband, trusted by both sides to be fair and honest.
There was one major incident during the years of Mara's marriage. In 1438 Đurađ got uppity. Murad really wanted to attack the Hungarian Empire, and while Đurađ promised to remain neutral in the conflict, he refused to allow the Ottoman armies into his territory. Murad wasn't too pleased about this. He started conquering Serbia, taking almost the entire country, and sending Đurađ running to Venice.
Murad wasn't satisfied with taking Serbia. He wanted revenge, and so in 1439 he captured Mara's brother, the heir apparent, Gregory. Gregory joined his brother Stefan, who had been held as a hostage since Mara's marriage six years earlier. Murad made Gregory the governor of several Serbian territories, but in 1440 became suspicious that Gregory was corresponding with his father. Gregory and Stefan were thrown into prison, in May of 1441 the pair were blinded, then released.²
Mara was, reportedly, furious. The Sultan had ordered that she not be told about the deed until after it was done. When she found out she reportedly threw her husband under her feet, screaming at him, making it more than clear that he had gone too far this time. Regretting his actions, Murad ordered that the person who blinded the brothers also be blinded as recompense. Because that would certainly rectify the situation.
This incident gives an interesting insight into Mara's relationship with her husband. It's clear that Murad not only respected Mara, but also considered her to be an equal to him, or at least an almost equal. He was evidently in fear of her wrath, where so many other men of the time had no regard for their wives' feelings on anything. This raises the question of if he considered Mara's political influence too great for him to risk offending her, or if he genuinely cared for her, and valued her good opinion.³
In 1444 the conflict between Serbia, Hungary, and the Ottomans was put to rest, with Mara playing a not insignificant part in the proceedings. After a few months of peace Murad abdicated, leaving his thirteen year old son, Mehmed II, in charge of the country. Murad, Mara, and a few other companions retreated to the countryside, with Murad coming out of retirement every so often to conquer important bits of land for his son. He died of an apoplexy in 1451.
This left the twenty year old Mehmed the sole Sultan in the empire. He and Mara were very close, she had become a sort of surrogate mother to him after his own mother died in 1449. When Mara asked to return to Serbia after her husband's death, Mehmed was more than happy to let her go, taking the extraordinary step of releasing her from the harem.
It must be noted that Mara and Mehmed's relationship would have been vastly different had she had children. Ottoman princes were notoriously fratricidal, with Mehmed himself making it legal to kill a brother who was in line for the throne. Any child of Mara's would have been a threat to Mehmed, and he could not have risked letting Mara or her child out of the country. Fortunately, Mara was childless, and posed very little threat.
Mara returned to her family in Serbia, all of whom were remarkably still alive, if not still in possession of all important organs. With Mara returned the vast swathes of Serbia that had served as her dowry, and Đurađ found himself the happy owner of more land than he had before.
From here, Đurađ did what medieval kings did best, arranged strategic marriages for his daughters to cement alliances between kingdoms. While Mara was getting on a bit, being somewhere between 32 and 39 years of age, she was still a valuable marriage candidate, especially given her Ottoman connections. Đurađ eagerly betrothed her to the last Byzantine Emperor, Emperor Constantine XI⁴
Unfortunately for Đurađ, Mara had had it with marriage. After Murad's death she had vowed never to marry again. Remarkably, her father (and later brothers) respected this vow, and she refused not only the Byzantine Emperor, but important Czech nobleman and ally against the Hungarians, Jana Jiskru.
When Đurađ died in 1456 a power struggle between his sons ensued. Gregory, the eldest brother, backed by Mara, Irene, and their powerful uncle Thomas, was challenged by Lazar, the youngest brother, backed by his wife and Stefan. Infighting grew so terrible that Irene died, and Mara returned to the Ottoman Empire.
Mara was welcomed back with open arms. She was given several towns and properties, and retired to Ježevo,⁵ near Mount Athos in modern Greece. It is notable that she retired to this area, as women were, and still are, forbidden to approach Mount Athos. Mara was the second woman ever to enter the area, and had to receive special permission from the monks in the area. However, given that she owned many of the monasteries, getting permission must have been easy enough.
It was, however, less easy for Mara to get her sister, Katrina to Ježevo. When Katrina's husband died in 1456, Katrina divided up his property, and peaced out of Hungary. She appears to have moved with her sister to Macedonia, though if they were in modern Greece Macedonia, or North Macedonia is uncertain.
From their home, the sisters played mediator between the powerful Republic of Venice and the Ottoman Empire during the Venetian-Turkish war of 1463-79. The Venetians sent their emissaries to the sisters, and the sisters would pass on their messages, or accompany the emissaries to Constantinople themselves. They took the further step of using Mount Athos, essentially a neutral ground, for negotiations between the two countries.
Mara's other notable political interventions involved the election of the Patriarch of the Eastern Orthodox Church. In Mehmed's time becoming Patriarch involved paying an obscene amount of money to be appointed by the Sultan. In 1465, Mara convinced Mehemed to appoint her personal priest, Dionysius, as patriarch. Unfortunately, Dionysius didn't last long in the role, but Mara was able to see him peacefully retired to Mount Athos. She tried again with Rafael, a Serbian monk, but he was unable to raise the required funds, and was reduced to begging in the streets of Constantinople.
Mara died peacefully in 1487, and was buried in the Kosinitza monastery. She left behind her a large amount of wealth and religious relics, which was vigorously fought over by her family. She also left behind a legacy of diplomacy and peacemaking. Her advocation for the rights of Christians in the Ottoman Empire lead to some small amount of peace between the groups, and her interventions with the Venetian Republic led to a few decades of tenuous peace.
¹The term 'Despot' is not commentary on Đurađ's ruling skills, but is, instead, the official title of the ruler of Serbia at the time.
²Other stories claim that the Sultan had the brothers blinded over jealousy. The brothers were excellent hunters, and Murat apparently couldn't stand that.
³Or, perhaps, he simply didn't like to be yelled at. That should also be taken into consideration.
⁴For those protesting that the Byzantine Empire and the Ottoman Empire are the same thing, it should be known that Istanbul was not always Constantinople. The Ottoman conquest of Byzantium was not complete until 1453.
⁵It has been difficult for this historian to ascertain exactly where and what Ježevo was. There is a city called Ježevo in modern Croatia, but as far as this historian can tell, it is not the city Mara settled in. Given Mara's involvement in Ottoman affairs, it seems unlikely that she would have settled as far away as Croatia. Additionally, Mara was heavily involved with affairs on Mount Athos, a holy mountain near Thessaloniki, Greece. It seems likely that Ježevo was the name of a small village, or even the name of Mara's estate near there.
This article is gratefully dedicated to M. Kellogg, who inspired and encouraged its development.
Article updated in 2019 to reflect the name change of North Macedonia. Formerly known as the "Former Yugoslav Republic of Macedonia", this country became North Macedonia in February of 2019.
Sources
Serbian Ladies and Athonite Monks by V. Demetriades and E. A. Zachariadou
Shedding New Light on the Ties of Mara Branković to the Holy Mountain of Athos and the Translation of Relics by Mihailo St. Popović
The Byzantine Lady: Ten Portraits, 1250-1500 by Donald M. Nicol
Serbia
Mara Brankovic
 |
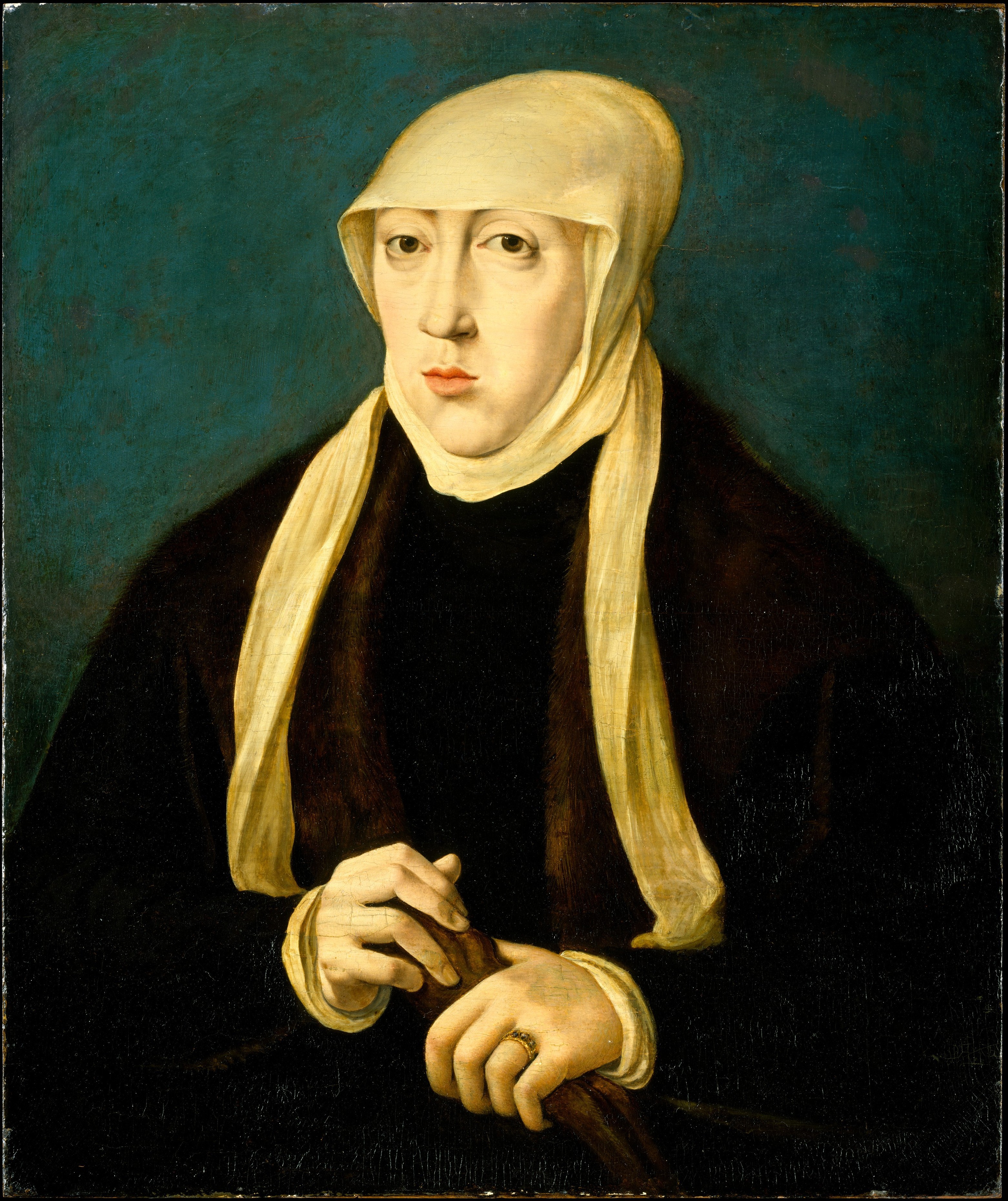
| The only known portrait of Mara. |
Mara was the daughter of Đurađ Branković and his second wife, Irene. Maybe. She may have been the daughter of Đurađ's first, unnamed wife. The documentation is shaky, and it's difficult to know exactly when and to whom Mara was born. What is for sure is that she was the second of five children--two girls and three boys.
Serbia, at the time, was in a shaky spot. Sandwiched between the rapidly growing Ottoman Empire, and the land hungry Hungarian Empire, Serbia was put in the precarious position of having to serve two masters who didn't like each other. Đurađ had been able to gain the position of despot by only the skin of his teeth, after the previous despot died without an heir. he required the approval of the leaders of his powerful neighbors to retain his position. In order to appease the pair, he gave his daughters to them in marriage, Mara to Sultan Murad II, and her sister, Katrina, to the Count of Hungary.
Mara was 21 at the age of her marriage in 1433. The sultan was fifteen years older than her, and already had a wife and an heir. Murad supposedly wasn't initially too keen on marrying the daughter of his lowly client king, but when her father offered most of Serbia as a dowry, Murad seized on the opportunity.
The years of Mara's marriage were fairly quiet. Murad favored Mara, but reportedly never consummated the relationship. Mara got on well with Murad's other wife, and his son. She served as an intermediary between her father and her husband, trusted by both sides to be fair and honest.
 |
| Murad II |
Murad wasn't satisfied with taking Serbia. He wanted revenge, and so in 1439 he captured Mara's brother, the heir apparent, Gregory. Gregory joined his brother Stefan, who had been held as a hostage since Mara's marriage six years earlier. Murad made Gregory the governor of several Serbian territories, but in 1440 became suspicious that Gregory was corresponding with his father. Gregory and Stefan were thrown into prison, in May of 1441 the pair were blinded, then released.²
Mara was, reportedly, furious. The Sultan had ordered that she not be told about the deed until after it was done. When she found out she reportedly threw her husband under her feet, screaming at him, making it more than clear that he had gone too far this time. Regretting his actions, Murad ordered that the person who blinded the brothers also be blinded as recompense. Because that would certainly rectify the situation.
This incident gives an interesting insight into Mara's relationship with her husband. It's clear that Murad not only respected Mara, but also considered her to be an equal to him, or at least an almost equal. He was evidently in fear of her wrath, where so many other men of the time had no regard for their wives' feelings on anything. This raises the question of if he considered Mara's political influence too great for him to risk offending her, or if he genuinely cared for her, and valued her good opinion.³
 |
| Mehmed II, later known as 'Mehmed the Conqueror' |
This left the twenty year old Mehmed the sole Sultan in the empire. He and Mara were very close, she had become a sort of surrogate mother to him after his own mother died in 1449. When Mara asked to return to Serbia after her husband's death, Mehmed was more than happy to let her go, taking the extraordinary step of releasing her from the harem.
It must be noted that Mara and Mehmed's relationship would have been vastly different had she had children. Ottoman princes were notoriously fratricidal, with Mehmed himself making it legal to kill a brother who was in line for the throne. Any child of Mara's would have been a threat to Mehmed, and he could not have risked letting Mara or her child out of the country. Fortunately, Mara was childless, and posed very little threat.
Mara returned to her family in Serbia, all of whom were remarkably still alive, if not still in possession of all important organs. With Mara returned the vast swathes of Serbia that had served as her dowry, and Đurađ found himself the happy owner of more land than he had before.
From here, Đurađ did what medieval kings did best, arranged strategic marriages for his daughters to cement alliances between kingdoms. While Mara was getting on a bit, being somewhere between 32 and 39 years of age, she was still a valuable marriage candidate, especially given her Ottoman connections. Đurađ eagerly betrothed her to the last Byzantine Emperor, Emperor Constantine XI⁴
 |
| The Ottoman Empire |
When Đurađ died in 1456 a power struggle between his sons ensued. Gregory, the eldest brother, backed by Mara, Irene, and their powerful uncle Thomas, was challenged by Lazar, the youngest brother, backed by his wife and Stefan. Infighting grew so terrible that Irene died, and Mara returned to the Ottoman Empire.
Mara was welcomed back with open arms. She was given several towns and properties, and retired to Ježevo,⁵ near Mount Athos in modern Greece. It is notable that she retired to this area, as women were, and still are, forbidden to approach Mount Athos. Mara was the second woman ever to enter the area, and had to receive special permission from the monks in the area. However, given that she owned many of the monasteries, getting permission must have been easy enough.
It was, however, less easy for Mara to get her sister, Katrina to Ježevo. When Katrina's husband died in 1456, Katrina divided up his property, and peaced out of Hungary. She appears to have moved with her sister to Macedonia, though if they were in modern Greece Macedonia, or North Macedonia is uncertain.
 |
| Monastery of Simonos Petra, located on Mount Athos. |
Mara's other notable political interventions involved the election of the Patriarch of the Eastern Orthodox Church. In Mehmed's time becoming Patriarch involved paying an obscene amount of money to be appointed by the Sultan. In 1465, Mara convinced Mehemed to appoint her personal priest, Dionysius, as patriarch. Unfortunately, Dionysius didn't last long in the role, but Mara was able to see him peacefully retired to Mount Athos. She tried again with Rafael, a Serbian monk, but he was unable to raise the required funds, and was reduced to begging in the streets of Constantinople.
Mara died peacefully in 1487, and was buried in the Kosinitza monastery. She left behind her a large amount of wealth and religious relics, which was vigorously fought over by her family. She also left behind a legacy of diplomacy and peacemaking. Her advocation for the rights of Christians in the Ottoman Empire lead to some small amount of peace between the groups, and her interventions with the Venetian Republic led to a few decades of tenuous peace.
¹The term 'Despot' is not commentary on Đurađ's ruling skills, but is, instead, the official title of the ruler of Serbia at the time.
²Other stories claim that the Sultan had the brothers blinded over jealousy. The brothers were excellent hunters, and Murat apparently couldn't stand that.
³Or, perhaps, he simply didn't like to be yelled at. That should also be taken into consideration.
⁴For those protesting that the Byzantine Empire and the Ottoman Empire are the same thing, it should be known that Istanbul was not always Constantinople. The Ottoman conquest of Byzantium was not complete until 1453.
⁵It has been difficult for this historian to ascertain exactly where and what Ježevo was. There is a city called Ježevo in modern Croatia, but as far as this historian can tell, it is not the city Mara settled in. Given Mara's involvement in Ottoman affairs, it seems unlikely that she would have settled as far away as Croatia. Additionally, Mara was heavily involved with affairs on Mount Athos, a holy mountain near Thessaloniki, Greece. It seems likely that Ježevo was the name of a small village, or even the name of Mara's estate near there.
This article is gratefully dedicated to M. Kellogg, who inspired and encouraged its development.
Article updated in 2019 to reflect the name change of North Macedonia. Formerly known as the "Former Yugoslav Republic of Macedonia", this country became North Macedonia in February of 2019.
Sources
Serbian Ladies and Athonite Monks by V. Demetriades and E. A. Zachariadou
Shedding New Light on the Ties of Mara Branković to the Holy Mountain of Athos and the Translation of Relics by Mihailo St. Popović
The Byzantine Lady: Ten Portraits, 1250-1500 by Donald M. Nicol
Serbia
Mara Brankovic