Militant and ruthless, Isabella of France was the sort of queen HBO and Starz make television shows about. Married at twelve, Isabella spent the early years of her reign being scorned and passed over for her husband's male favorites. Forced to stand between her husband, his aristocracy, and England, Isabella became a wily diplomat and politician, which later saw her ousting her corrupt and weak husband with the help of her lover. Though she saw real power for only four years, she saw her son onto the throne, and was instrumental in holding England together during the tumultuous years of Edward II. Deemed 'the she-wolf of France'¹, Isabella was a fierce defender of what was hers.
Born sometime between 1292 and 1295, Isabella was the sixth child and only surviving daughter of King Philip the Fair of France, and Queen Jeanne of Navarre. Very early in her life Isabella was given into the care of Theophania St. Pierre, who served as her nurse and companion even after her marriage.
Despite being cared for by Theophania, Isabella was, in no way, neglected by her parents. As their only girl she was much indulged, and given several grants of land, making her wealthy even as a child. In addition to being given land, Isabella was also given a rudimentary education,being taught to read even though her father generally held the belief that only nuns should be taught to read. Isabella developed a love of books and learning that would sustain her throughout her life.
It is important to note the sort household that Isabella was raised in. While by no means normal, Isabella's family was idyllic by the standards of the times, and the modern day. Her parents were in love, and it was very likely that their marriage had been a love match. Isabella's mother ran her country, Navarre, independent of Philip's France, and Philip was a strong, if somewhat brutal, king of France. Isabella was raised by exemplary monarchs with strong relationship. This would stand in stark contrast to the men in her own future, and may have contributed to the disillusionment that Isabella would experience later in her life.
At the time of Isabella's birth France and England were, unsurprisingly, at war. Traditional enemies, England and France's latest quarrel was over the regions of Aquitaine and Gascony, regions that the two countries had been fighting over since Eleanor of Aquitaine's marriage to Henry II, and the transfer of her lands to English hands, four generations previous. Philip IV and Edward I were ready to call a temporary truce, and they decided to seal the deal with a double marriage--Philip's sister, Margaret of France, to Edward I, and Edward I's son, Edward of Caernarvon, to Philip's only daughter, Isabella.
The marriage was agreed to in 1298, and Edward pressed for Isabella to marry his son immediately, but an intervention from Pope Boniface VIII, proposing that marrying off a three year old was perhaps a little unethical, delayed the union. The couple were married by proxy when Isabella was seven, then married for real in 1308.
Twelve year old Isabella was hailed as a beauty, and was greeted joyously by her new English public. Her husband, Edward, however, wasn't as enthused. It wasn't that he disliked Isabella, it was just that he was enamoured with another man, and he was completely indifferent to the twelve year old he had just vowed to love, honor, and obey. Edward already had someone to love, honor, and obey, his husband favorite, Piers Gaveston.
Piers Gaveston and Edward II went all the way back to 1300, when Edward was 15 (ish). Edward's father, Edward (hereafter referred to as 'Big Daddy Ed'), wasn't too terribly impressed with his son. Big Daddy Ed was a Medieval King's Medieval King. His hobbies included holding tournaments, producing heirs, and warring with the Scots. Edward, on the other hand, liked music, swimming, rowing, and thatching. Big Daddy Ed was disgusted with his son, and so he installed Piers Gaveston, the son of a poor knight, in Edward's household. Piers was the sort of fellow that Big Daddy Ed would have liked to have for a son--athletic, refined, and a great lover of warring with the Scots. He'd hoped that Piers would be an improving influence for his son, unfortunately, Piers was anything but. Piers and Edward fell in love almost immediately, and the pair proceeded to wreak havoc among the nobility and common people.
While Piers doesn't appear to have been present at Edward and Isabella's marriage, he was most notably present at their coronation (Big Daddy Ed having died a few months before). Piers had controversially been raised to the title of Earl of Cornwall², and as such had the right to wear cloth of gold at the coronation. Piers, however, decided to show up in purple silk, essentially claiming status on par with Isabella and Edward. He also proceeded Isabella and Edward in the procession, and was given several other prestigious duties during the ceremony. This infuriated Edward's nobles, as Piers was, outside of his flashy new titles, not particularly blue-blooded.
The real insults came at the banquet succeeding the coronation. Edward had been given substantial sums of money by the French for the coronation, and had spent it on lavish tapestries displaying the arms of himself and Gaveston. Edward took several of the jewels and wedding presents meant for Isabella, and gave them to Gaveston, and spent much of the evening with hishusband favorite, instead of with his new bride. The French delegation was outraged, and Isabella wrote to her father that she felt like a nonentity in her own marriage.
For the first few years of her marriage, Isabella had very little political power, and much of the drama and intrigue of this time concerns Edward and Piers. Edward burned through goodwill and money quickly, and had alienated his nobility not long after his coronation. His continued indulgence and promotion of Gavestone, as well as his neglect of the kingdom and ineffectual warring with the Scots, led his barons to draw up the Ordinances of 1311, which severely curtailed his powers. He was forced to banish Gaveston multiple times, but always managed to recall him at a later date. Isabella more or less was dragged along with them, with very little power of her own. However, everything changed when Isabella turned sixteen.
There was no formal agreement about what age Isabella had to reach before she and Edward would consummate their marriage, but even in Medieval times it was generally agreed upon that getting pregnant at twelve was sheer dangerous idiocy. Getting pregnant at sixteen, however, was merely dangerous. Consequently, Isabella was pregnant by 1312.
Now, at this time Edward and Gaveston were in the middle of yet another one of their power struggles with the English aristocracy. Gaveston had been exiled again in 1311, and his return to England had ruffled more than a few feathers. Additionally, the Scots were feeling frisky again, and they were making war in Northern England.
Unfortunately, Northern England was where Isabella was, and her husband's war making was so incompetent, that she soon found herself in danger. Edward marched south with his army, leaving Isabella with scant protection from the advancing Scots.
Isabella and Edward both made it safely back to London, but Gaveston was not as fortunate. He had been trapped in Scarborough Castle by his enemies, and executed, leaving Edward bitter and heartbroken. On November 13th Isabella's first child, the future Edward III, was born.
The next four years would be the happiest of Edward and Isabella's marriage. Two of their four living children--John and Eleanor--were born during this period. During this time Edward put significant efforts into repairing his relationships with his subjects, enacting reforms and reassigning lands that had been unfairly given to Gavestone. Edward seemed contrite, and for a time England enjoyed a brittle peace. However, things grew uneasy as another royalboyfriend favorite rose over the horizon.
The Despenser family were related to Edward, and Hugh Despenser the Younger (Hereafter known as 'Horny Hugh') was technically Edward's nephew. In 1318, Horny Hugh was made Edward's royal chamberlain. Horny Hugh Despenser and his father, Hugh Despenser, both had political ambitions. Unlike Gavestone, who was content to be a wealthy, lowborn, nuisance, Horny Hugh wanted to rule. He was given large swathes of the marchlands, angering the Marcherlords³ to whom the land rightfully belonged.
Furthermore, Horny Hugh and Isabella didn't like each other. It's unknown what sort of relationship Isabella had had with Gavestone, but given that Isabella was little more than a child during Gavestone's tenure as royalhusband favorite, it seems likely that they didn't have much of a relationship at all.
However, with Horny Hugh, things were different. Isabella was becoming a political person in her own right, and she was painfully aware that Horny Hugh and the Despensers elevation insulted her, her French family, and the realm. She was frequently called upon by the barons to curb the king's worst impulses, and her and Edward's relationship grew increasingly tense. In 1322 Edward asked Isabella to swear an oath of loyalty to the Despensers. When she refused, he took away her lands, and gave custody of their two youngest children--Eleanor and Joan--to Horny Hugh.
Meanwhile, Isabella's brother Charles had become King of France, and he was eyeing Gascony with increasing amounts of lust. Squabbles started popping up in the region, and despite multiple attempts at diplomacy, including sending Edward and Isabella's eldest son to France, war seemed inevitable. In 1325, Edward decided to send Isabella to intercede.
Once back in France, Isabella had very little reason to be loyal to Edward. He had taken her children, confiscated her lands, and reduced her to little more than a pauper. She had been insulted and humiliated for seventeen years, and she was done. Safe at her brother's court in Paris, Isabella declared her contempt for her husband and the Despensers. She took up the garb of a widow, saying, essentially, that her husband was dead to her, and that she considered him unfit for the office he held. With the help of her cousins in the Lowlands, Isabella began plotting to remove Edward from the son in favor of their eldest son.
Enter Roger Mortimer. He was a young, handsome nobleman with vast estates in Wales and Ireland. He had been exiled from England for his political policies of attempting to overthrow the Despensers, and he had a thirst for vengeance. He and Isabella had met many times before, as Mortimer had been a regular at court, but with Isabella in widow weeds, and Mortimer driven from his home, something had changed. They began to plot together, and that plotting soon moved to the bedchamber, where it is widely assumed that they began plotting Edward's overthrow in a horizontal position.
Roger and Isabella's relationship is an interesting one. It is quite obvious that she was very enamored of him. She was permissive of his bad behavior far beyond what someone using him as a means to an end would have been. However, it is difficult to ascertain Mortimer's feelings. While they had some things in common--love of art, love of Arthurian Romance--he frequently disregarded her wishes concerning their plot, and later the running of the country. After attaining the regency, he used her to gain vast lands and wealth. This may be constructed just as him being the typical medieval man, but there was also the fact that Mortimer was already married to a woman it was widely rumored to be in love with. However, he and his wife had been separated for three years, and it was possible that his ardor towards his wife had cooled, and he truly had feelings for Isabella.
Though they were nowhere near as open about it as Edward and hishusbands favorites, it soon became common knowledge that Isabella and Mortimer were lovers. This enraged Edward, who swore that if he saw Isabella again he would kill her. Because of her adultery, Isabella's brother refused to help her with her coup.⁴ Luckily, Isabella's cousins in Hainault⁵ held no such compunctions, and gave them ships and Dutch mercenaries to begin their invasion.
Isabella and Mortimer landed in Suffolk in September of 1326. Edward's few allies quickly abandoned him, and England was taken with almost no bloodshed. Horny Hugh was hanged, drawn, and quartered, and Edward was deposed and imprisoned in Berkeley Castle. Isabella and Edward's eldest son, Edward (hereafter referred to as 'Baby Edward'), was placed on the throne.
As Baby Edward was only fourteen, a regency was necessary. As queen, this position was granted to Isabella, and she, along with Mortimer, would serve as regents for about four years.
About a year into their regency, Isabella and Mortimer decided to deal with the problem of the old king. Despite imprisoning him in a dank dungeon, and throwing dead animals and rotting corpses into his cell in hopes he would die of disease, Edward stubbornly remained alive. He remained a rallying point for those who opposed Isabella and Mortimer, and in September of 1327, he mysteriously died.
Unfortunately, their regency wasn't entirely popular. Isabella herself remained widely respected, it was Mortimer who was the problem. Like all of the other husbands favorites in Isabella's story, Mortimer was greedy and grasping; sending England to the brink of bankruptcy to enrich himself. He was very unpopular, and Baby Edward grew resentful.
In 1330 Edward had had enough. With support of Henry of Lancaster, Edward staged a dramatic midnight coup, taking a secret passage into the castle where his mother and Mortimer were living, pinning them and their advisors in an enclosed chamber, forcing them to abdicate. Mortimer was hanged a short while later, while Isabella was placed under house arrest.
There were several people who called for Isabella's execution, but Edward declined, instead spinning the narrative that she was innocent in the affair, and that the blame rested squarely with Mortimer. Her lands were seized, and she was pensioned off, placed under house arrest at Castle Rising in the Norfolk countryside where she couldn't cause any more problems.
The last years of Isabella's life saw her growing closer to her family, and finding religion. Her daughter, Joan, came to live with her after leaving her husband, and Isabella doted ceaselessly on her grandchildren. Towards the end of her life, she and Baby Edward reconciled. She became a nun in 1358, and died shortly after.
Looking at her life, it can be difficult to determine if Isabella was a plotting villainess or a woman making bloody, bloody lemonade. It is apparent that she struggled for much of her life to become an active agent in her own fate, and was met with mixed success. Today she is mostly forgotten, lost in the blinding glare of her son, Edward III, who is frequently touted as being England's greatest king. However, she should be remembered as a brilliant queen and stateswoman in her own right, who was instrumental in ensuring stability in England, even if she had to do it by force.
¹The title was borrowed from Shakespeare's play Henry IV, Part III. The original title referred to Margaret of Anjou, but has since become a byname for Isabella.
²This caused a major scandal, because the Earldom of Cornwall was then, and now, a royal title. (It's currently held as an auxiliary title of Prince Charles.) While Cornwall is no longer an Earldom but a Dukedom, it is still considered to be the right of the first born son of the monarch.
³A Marcherlord was a nobleman with holdings along the border with Wales, who was expected to defend the border.
⁴Adultery was a major crime for a Medieval noblewoman. Charles' first wife had committed adultery, and Charles had had her lovers beaten to death in a public square. It is unsurprising that he was less than permissive about his sister's liaison with Roger Mortimer.
⁵The aforementioned Lowland cousin. Coincidentally, this same cousin, Joan of Hainault, was responsible for throwing Isabella and Mortimer together.
⁶This story was later used to support the causes of people who would rebel against Baby Edward.
Sources
The Plantagenets by Dan Jones
Queen Isabella: Treachery, Adultery, and Murder in Medieval England by Alison Weir
She-Wolves: The Women Who Ruled England Before Elizabeth by Helen Castor
Isabella, the 'She-Wolf of France'
Edward II Marries Isabella of France
Isabella of France: Queen of England
Isabella of France
Edward II: King of England
Edward II:1307-1327
Edward II (1284-1327)
Edward II:1307-1327 AD
Piers Gaveston, Hugh Despenser, and the Downfall of Edward II
Roger Mortimer
Edward III
 |
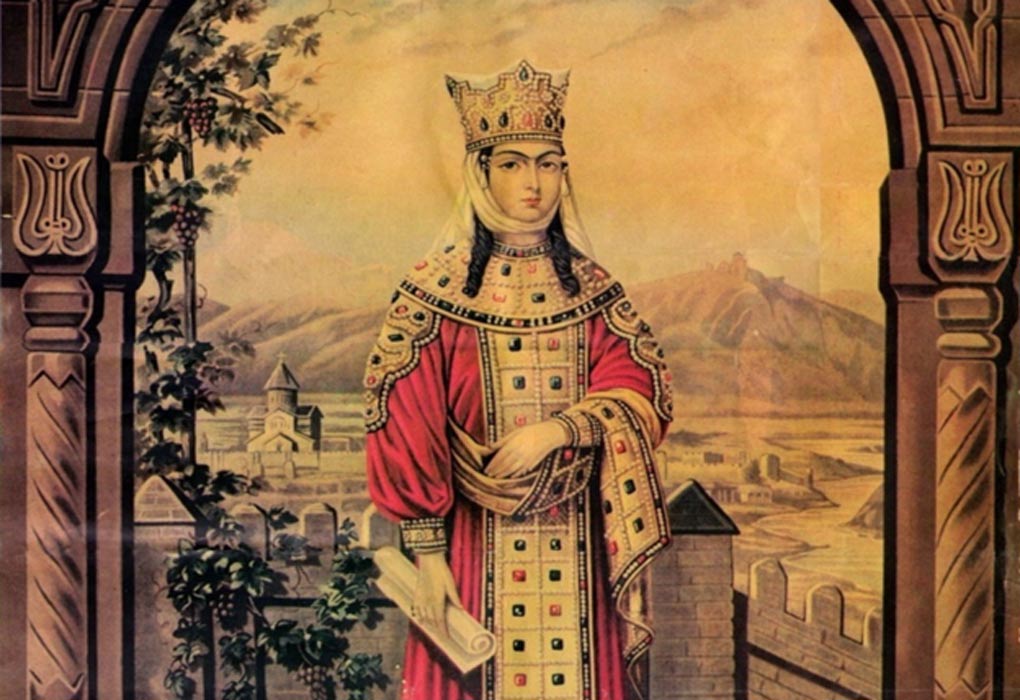
| Our girl Isabella, deciding the fate of her enemies. |
Despite being cared for by Theophania, Isabella was, in no way, neglected by her parents. As their only girl she was much indulged, and given several grants of land, making her wealthy even as a child. In addition to being given land, Isabella was also given a rudimentary education,being taught to read even though her father generally held the belief that only nuns should be taught to read. Isabella developed a love of books and learning that would sustain her throughout her life.
It is important to note the sort household that Isabella was raised in. While by no means normal, Isabella's family was idyllic by the standards of the times, and the modern day. Her parents were in love, and it was very likely that their marriage had been a love match. Isabella's mother ran her country, Navarre, independent of Philip's France, and Philip was a strong, if somewhat brutal, king of France. Isabella was raised by exemplary monarchs with strong relationship. This would stand in stark contrast to the men in her own future, and may have contributed to the disillusionment that Isabella would experience later in her life.
At the time of Isabella's birth France and England were, unsurprisingly, at war. Traditional enemies, England and France's latest quarrel was over the regions of Aquitaine and Gascony, regions that the two countries had been fighting over since Eleanor of Aquitaine's marriage to Henry II, and the transfer of her lands to English hands, four generations previous. Philip IV and Edward I were ready to call a temporary truce, and they decided to seal the deal with a double marriage--Philip's sister, Margaret of France, to Edward I, and Edward I's son, Edward of Caernarvon, to Philip's only daughter, Isabella.
The marriage was agreed to in 1298, and Edward pressed for Isabella to marry his son immediately, but an intervention from Pope Boniface VIII, proposing that marrying off a three year old was perhaps a little unethical, delayed the union. The couple were married by proxy when Isabella was seven, then married for real in 1308.
 |
| Edward Caernarvon at his coronation. |
Piers Gaveston and Edward II went all the way back to 1300, when Edward was 15 (ish). Edward's father, Edward (hereafter referred to as 'Big Daddy Ed'), wasn't too terribly impressed with his son. Big Daddy Ed was a Medieval King's Medieval King. His hobbies included holding tournaments, producing heirs, and warring with the Scots. Edward, on the other hand, liked music, swimming, rowing, and thatching. Big Daddy Ed was disgusted with his son, and so he installed Piers Gaveston, the son of a poor knight, in Edward's household. Piers was the sort of fellow that Big Daddy Ed would have liked to have for a son--athletic, refined, and a great lover of warring with the Scots. He'd hoped that Piers would be an improving influence for his son, unfortunately, Piers was anything but. Piers and Edward fell in love almost immediately, and the pair proceeded to wreak havoc among the nobility and common people.
While Piers doesn't appear to have been present at Edward and Isabella's marriage, he was most notably present at their coronation (Big Daddy Ed having died a few months before). Piers had controversially been raised to the title of Earl of Cornwall², and as such had the right to wear cloth of gold at the coronation. Piers, however, decided to show up in purple silk, essentially claiming status on par with Isabella and Edward. He also proceeded Isabella and Edward in the procession, and was given several other prestigious duties during the ceremony. This infuriated Edward's nobles, as Piers was, outside of his flashy new titles, not particularly blue-blooded.
The real insults came at the banquet succeeding the coronation. Edward had been given substantial sums of money by the French for the coronation, and had spent it on lavish tapestries displaying the arms of himself and Gaveston. Edward took several of the jewels and wedding presents meant for Isabella, and gave them to Gaveston, and spent much of the evening with his
For the first few years of her marriage, Isabella had very little political power, and much of the drama and intrigue of this time concerns Edward and Piers. Edward burned through goodwill and money quickly, and had alienated his nobility not long after his coronation. His continued indulgence and promotion of Gavestone, as well as his neglect of the kingdom and ineffectual warring with the Scots, led his barons to draw up the Ordinances of 1311, which severely curtailed his powers. He was forced to banish Gaveston multiple times, but always managed to recall him at a later date. Isabella more or less was dragged along with them, with very little power of her own. However, everything changed when Isabella turned sixteen.
There was no formal agreement about what age Isabella had to reach before she and Edward would consummate their marriage, but even in Medieval times it was generally agreed upon that getting pregnant at twelve was sheer dangerous idiocy. Getting pregnant at sixteen, however, was merely dangerous. Consequently, Isabella was pregnant by 1312.
 |
| Map of the British Isles in 1300. Not included are the Plantagenet lands in southern France. |
Unfortunately, Northern England was where Isabella was, and her husband's war making was so incompetent, that she soon found herself in danger. Edward marched south with his army, leaving Isabella with scant protection from the advancing Scots.
Isabella and Edward both made it safely back to London, but Gaveston was not as fortunate. He had been trapped in Scarborough Castle by his enemies, and executed, leaving Edward bitter and heartbroken. On November 13th Isabella's first child, the future Edward III, was born.
The next four years would be the happiest of Edward and Isabella's marriage. Two of their four living children--John and Eleanor--were born during this period. During this time Edward put significant efforts into repairing his relationships with his subjects, enacting reforms and reassigning lands that had been unfairly given to Gavestone. Edward seemed contrite, and for a time England enjoyed a brittle peace. However, things grew uneasy as another royal
The Despenser family were related to Edward, and Hugh Despenser the Younger (Hereafter known as 'Horny Hugh') was technically Edward's nephew. In 1318, Horny Hugh was made Edward's royal chamberlain. Horny Hugh Despenser and his father, Hugh Despenser, both had political ambitions. Unlike Gavestone, who was content to be a wealthy, lowborn, nuisance, Horny Hugh wanted to rule. He was given large swathes of the marchlands, angering the Marcherlords³ to whom the land rightfully belonged.
Furthermore, Horny Hugh and Isabella didn't like each other. It's unknown what sort of relationship Isabella had had with Gavestone, but given that Isabella was little more than a child during Gavestone's tenure as royal
However, with Horny Hugh, things were different. Isabella was becoming a political person in her own right, and she was painfully aware that Horny Hugh and the Despensers elevation insulted her, her French family, and the realm. She was frequently called upon by the barons to curb the king's worst impulses, and her and Edward's relationship grew increasingly tense. In 1322 Edward asked Isabella to swear an oath of loyalty to the Despensers. When she refused, he took away her lands, and gave custody of their two youngest children--Eleanor and Joan--to Horny Hugh.
Meanwhile, Isabella's brother Charles had become King of France, and he was eyeing Gascony with increasing amounts of lust. Squabbles started popping up in the region, and despite multiple attempts at diplomacy, including sending Edward and Isabella's eldest son to France, war seemed inevitable. In 1325, Edward decided to send Isabella to intercede.
Once back in France, Isabella had very little reason to be loyal to Edward. He had taken her children, confiscated her lands, and reduced her to little more than a pauper. She had been insulted and humiliated for seventeen years, and she was done. Safe at her brother's court in Paris, Isabella declared her contempt for her husband and the Despensers. She took up the garb of a widow, saying, essentially, that her husband was dead to her, and that she considered him unfit for the office he held. With the help of her cousins in the Lowlands, Isabella began plotting to remove Edward from the son in favor of their eldest son.
 |
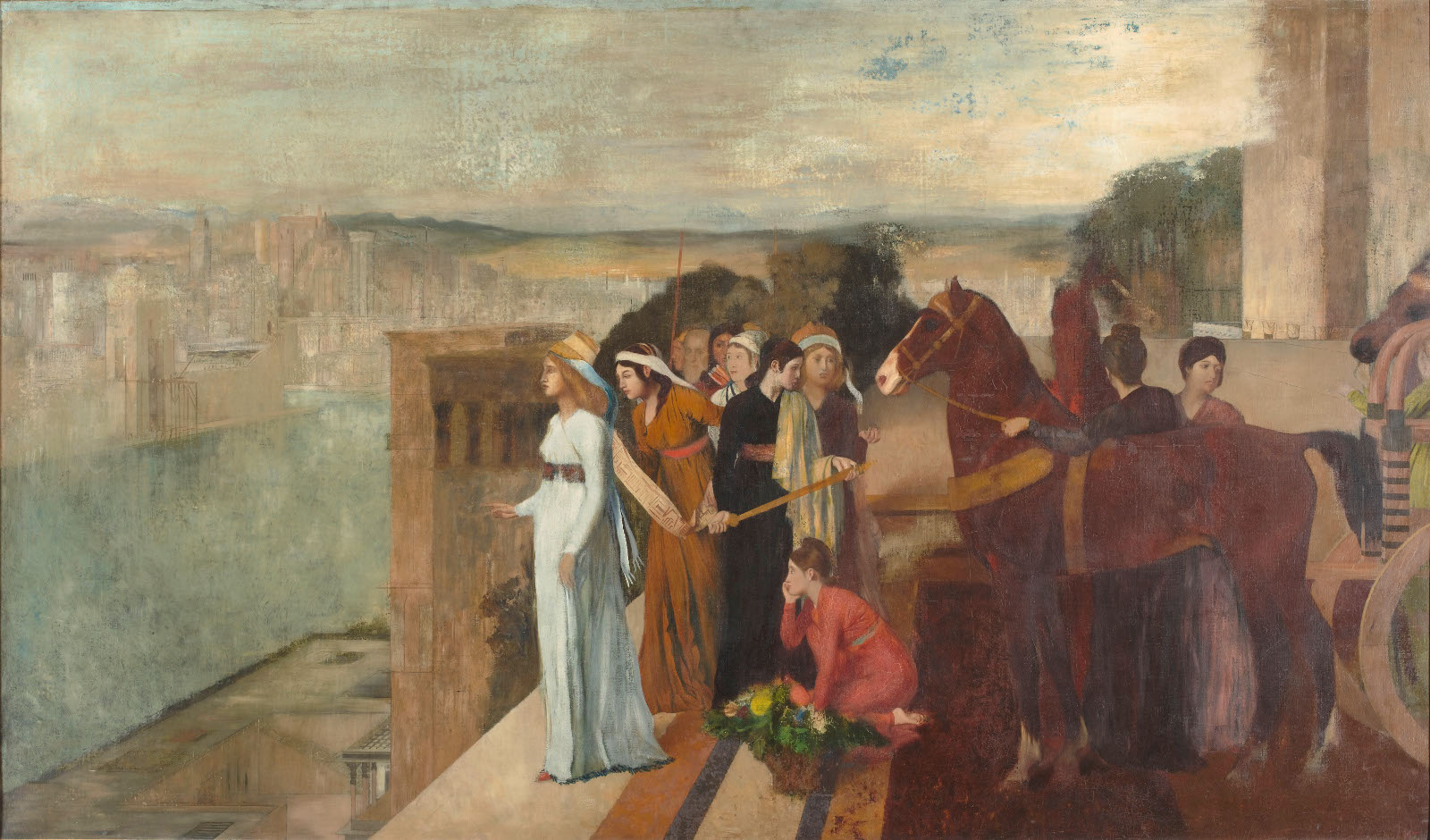
| Roger speaking with Isabella on a battlefield |
Roger and Isabella's relationship is an interesting one. It is quite obvious that she was very enamored of him. She was permissive of his bad behavior far beyond what someone using him as a means to an end would have been. However, it is difficult to ascertain Mortimer's feelings. While they had some things in common--love of art, love of Arthurian Romance--he frequently disregarded her wishes concerning their plot, and later the running of the country. After attaining the regency, he used her to gain vast lands and wealth. This may be constructed just as him being the typical medieval man, but there was also the fact that Mortimer was already married to a woman it was widely rumored to be in love with. However, he and his wife had been separated for three years, and it was possible that his ardor towards his wife had cooled, and he truly had feelings for Isabella.
Though they were nowhere near as open about it as Edward and his
| Berkeley Castle, where Edward died. |
As Baby Edward was only fourteen, a regency was necessary. As queen, this position was granted to Isabella, and she, along with Mortimer, would serve as regents for about four years.
About a year into their regency, Isabella and Mortimer decided to deal with the problem of the old king. Despite imprisoning him in a dank dungeon, and throwing dead animals and rotting corpses into his cell in hopes he would die of disease, Edward stubbornly remained alive. He remained a rallying point for those who opposed Isabella and Mortimer, and in September of 1327, he mysteriously died.
There are a few stories about how Edward died. Least gruesome is that he was smothered in his sleep. Most popular is that a flaming hot poker was inserted into his anus, and run through his entrails. There are some stories as well that claim he didn't die, but instead escaped, and fled to Italy to live out the rest of his life as a monk.⁶ While neither Isabella nor Mortimer confessed to having ordered or committed the murders, it is widely assumed that they at the very least signed off on the order.
In 1330 Edward had had enough. With support of Henry of Lancaster, Edward staged a dramatic midnight coup, taking a secret passage into the castle where his mother and Mortimer were living, pinning them and their advisors in an enclosed chamber, forcing them to abdicate. Mortimer was hanged a short while later, while Isabella was placed under house arrest.
 |
| Baby Edward |
The last years of Isabella's life saw her growing closer to her family, and finding religion. Her daughter, Joan, came to live with her after leaving her husband, and Isabella doted ceaselessly on her grandchildren. Towards the end of her life, she and Baby Edward reconciled. She became a nun in 1358, and died shortly after.
Looking at her life, it can be difficult to determine if Isabella was a plotting villainess or a woman making bloody, bloody lemonade. It is apparent that she struggled for much of her life to become an active agent in her own fate, and was met with mixed success. Today she is mostly forgotten, lost in the blinding glare of her son, Edward III, who is frequently touted as being England's greatest king. However, she should be remembered as a brilliant queen and stateswoman in her own right, who was instrumental in ensuring stability in England, even if she had to do it by force.
¹The title was borrowed from Shakespeare's play Henry IV, Part III. The original title referred to Margaret of Anjou, but has since become a byname for Isabella.
²This caused a major scandal, because the Earldom of Cornwall was then, and now, a royal title. (It's currently held as an auxiliary title of Prince Charles.) While Cornwall is no longer an Earldom but a Dukedom, it is still considered to be the right of the first born son of the monarch.
³A Marcherlord was a nobleman with holdings along the border with Wales, who was expected to defend the border.
⁴Adultery was a major crime for a Medieval noblewoman. Charles' first wife had committed adultery, and Charles had had her lovers beaten to death in a public square. It is unsurprising that he was less than permissive about his sister's liaison with Roger Mortimer.
⁵The aforementioned Lowland cousin. Coincidentally, this same cousin, Joan of Hainault, was responsible for throwing Isabella and Mortimer together.
⁶This story was later used to support the causes of people who would rebel against Baby Edward.
Sources
The Plantagenets by Dan Jones
Queen Isabella: Treachery, Adultery, and Murder in Medieval England by Alison Weir
She-Wolves: The Women Who Ruled England Before Elizabeth by Helen Castor
Isabella, the 'She-Wolf of France'
Edward II Marries Isabella of France
Isabella of France: Queen of England
Isabella of France
Edward II: King of England
Edward II:1307-1327
Edward II (1284-1327)
Edward II:1307-1327 AD
Piers Gaveston, Hugh Despenser, and the Downfall of Edward II
Roger Mortimer
Edward III