Morris Dance is a type of English folk dance of mysterious origins. It was (and is) most frequently practiced through the midlands and in the counties along the Welsh border, but it has connections to folk dances throughout Western Europe. Morris dance is characterized by energetic stepping and skipping, as well as the use of bells, handkerchiefs, sticks, swords, and the occasional beast.
The first reference to Morris style dance comes from the wedding of Raymond Berengar, Duke of Barcelona, and Petronilla of Aragon in 1149. There are further references to continental Morris dances being adopted into church ceremonies and being performed at court events throughout the Middle Ages. It is very likely that these dances were being performed in England at the same time as well, as Morris dance was considered ancient by the Elizabethans.
The earliest mention of Morris dance in England dates from 1448, when a tapestry depicting Morris dancers was recorded in an inventory of Caister Castle. That same year, a troupe of Morris dancers were paid seven shillings by the Goldsmiths Guild for a St. Dunstan Day performance. There are several other records of Morris dancers appearing on objects, and being paid for performances throughout the fifteenth and sixteenth centuries.¹
The name "Morris" is generally seen to be as a corruption of the Spanish word "Morisco," referring to the Arabs who occupied Southern Europe throughout much of the Middle Ages. This has led many historians to assume that Morris dancing has its roots in the traditional dance of the Moriscos. However, as Morris dance bears minimal resemblance to Moorish traditional dance this theory has been discarded by modern historians.
Additionally, the name "Moorish" was a fashionable appendage to any art considered even a little bit foreign. New music, dances, and clothing styles were labeled as "Moorish," relationship to Middle Eastern culture or not. It seems most likely to this historian that the name "Morris" was given to the dance at a later date, perhaps as a way to further distance the dance from its pagan origins.
This brings us to the probably pagan origins of Morris dance. It is likely that Morris dance existed long before the Arabs made it to Europe, and instead evolved from pagan traditions. Many dances tell the stories of a battle against nature, and dances were performed on days that were culturally significant to pagans, such as the beginning of summer and the middle of winter. In addition, the appearances of hobbyhorses and the occasional dragon or unicorn also hint at a pagan past, as these animals could be seen as a focus of worship. Outside of England in Brittany some small churches had a festival specially dedicated to the hobbyhorse, where the horse was adorned with flowers and paraded around the town. Though this was a supposedly Christian festival, it certainly seems more pagan to outside observers.
The Morris dance of the Middle Ages can be split into two styles--Court Morris and Folk Morris. Morris dancing was very popular in the Tudor courts, with records of it having been performed in the courts of Henry VII and Henry VIII. Court Morris was an elaborate affair with expensive costumes and elaborate sets. The line between Morris and mumming is a thin one at best, but it was especially thin in these court dances with their elaborate costuming and pageantry.² Court Morris flourished until Oliver Cromwell and the Puritans took power in 1649.
Opposed to dancing, drinking, and anything resembling a good time, Cromwell suppressed Morris dance into near extinction. However, the tradition survived. Morris dance resurfaced in the countryside after the restoration of the English monarchy. Morris dancing had fallen out of favor with the nobility, but it was adopted by the commoners. The common people couldn't afford the same elaborate costuming as the nobility, but they used ribbons, bells, flowers and colorful rags to add to their appearance. The modern Morris costume evolved from their imitations.
However, as Britain industrialized the dance began to fall out of style. Many young men moved to the factory towns, and were disinclined to continue Morris dancing. Early twentieth-century Morris dancers lamented that the younger generation was too proud to continue the tradition, because it was too much like begging. These young men might have changed their minds as time wore on, but unfortunately, many of those young men lost their lives in World War I.
Morris dance may have been lost to time had it not been carefully documented by the ethnochoreologist and ethnomusicologist Cecil Sharp. Sharp traveled England collecting folk dances and published several works on the subject. Sharp's books revived interest in Morris dance, and Morris began to be taught (and tested) in some English schools.
A group of Morris dancers is called a side. Historically, Morris sides were exclusively male, but that is no longer the case. While a side can, hypothetically, consist of an infinite number of dancers, most have less than twenty, including the band. Most dances have only six to eight dancers on the floor at a time.
Traditional sides are led by a Squire who arranges performances and is generally the man in charge. Under him is the Foreman or Captain who teaches the dances. Last on the leadership hierarchy is the Bagman, who serves as a secretary. Under them are the dancers, and the occasional Fool or Beast.
Beasts are Morris characters that add to the story of the dance. Common beasts are hobbyhorses, dragons, and unicorns. It can be difficult for Beasts to dance with the same nimbleness as the other dancers due to their cumbersome costume, but that doesn't stop many from trying. Hobbyhorses are the most common type of Beasts in modern practice.
There are six main styles of Morris dance still practiced in England today: Cotswold, Molly, Border, Northwest Clog, Longsword, and Rapper. While all are related, each style has a unique flavor and tradition.
It would be remiss of this historian to write about Morris dance but not talk about the live music that often accompanies the dancers. Morris bands utilize traditional instruments (concertina, fiddle, melodian, accordion, pipes, tabor) and are percussion driven. Bands can range in size from a single musician to tens of people, depending on the style of dance and the preference of the side. Musicians often dress to match the dancers and are an integral part of the performance.
Morris dancing, particularly Border Style and Molly Dance Morris, have met with controversy in recent years due to the fact that many Morris sides include black face paint as a part of their costume. The tradition of dancers blackening their faces has dozens of explanations dating from different eras, but some of the most common are:
It seems likely that the reason for using face paint during Morris dances has changed throughout the ages, and there is no definitive reason for it. It must be mentioned, however, that wearing blackface in Morris dance predates the practice of wearing blackface in American minstrel shows. All the same, many Morris sides have abandoned the practice and either leave their faces bare or paint them a different color.
During its long history, Morris dance has transitioned from being an important pagan ritual, to being a way of making money, into a lighthearted celebration of English culture. Morris has evolved over the years, and undoubtedly will continue to do so, proving that culture and tradition are mutable.
¹One of the more colorful stories about Morris Dance from this era is that of the actor Will Kemp, who bet a friend that he could Morris dance from London to Norwich before the end of Lent. In a feat that would come to be known as his "Nine Day Wonder," Kemp danced the more than 100 miles between the two cities. While the entire journey took more than nine days, he did win his bet. While not the inspiration for, it is definitely reminiscent of Tony Hawks who, in the 1990s hitchhiked around the circumference of Ireland with a mini-fridge, also on a bet.
² The line was even thinner outside of England in Spain, where Morris dances often portrayed a battle between Christians and Muslims with the Christians emerging triumphant.
Sources
"Morris and Morisca" by Violet Alford
"Some Other Hobby Horses" by Violet Alford
"Early Record of the Morris in England" by Lucile Armstrong and Barbara Lowe
"The Origins of the Morris Dance" by Rodney Gallop
"The Abram Morris Dance" by Maud Karpeles
 |
| Morris dancer and musician. |
The earliest mention of Morris dance in England dates from 1448, when a tapestry depicting Morris dancers was recorded in an inventory of Caister Castle. That same year, a troupe of Morris dancers were paid seven shillings by the Goldsmiths Guild for a St. Dunstan Day performance. There are several other records of Morris dancers appearing on objects, and being paid for performances throughout the fifteenth and sixteenth centuries.¹
The name "Morris" is generally seen to be as a corruption of the Spanish word "Morisco," referring to the Arabs who occupied Southern Europe throughout much of the Middle Ages. This has led many historians to assume that Morris dancing has its roots in the traditional dance of the Moriscos. However, as Morris dance bears minimal resemblance to Moorish traditional dance this theory has been discarded by modern historians.
Additionally, the name "Moorish" was a fashionable appendage to any art considered even a little bit foreign. New music, dances, and clothing styles were labeled as "Moorish," relationship to Middle Eastern culture or not. It seems most likely to this historian that the name "Morris" was given to the dance at a later date, perhaps as a way to further distance the dance from its pagan origins.
This brings us to the probably pagan origins of Morris dance. It is likely that Morris dance existed long before the Arabs made it to Europe, and instead evolved from pagan traditions. Many dances tell the stories of a battle against nature, and dances were performed on days that were culturally significant to pagans, such as the beginning of summer and the middle of winter. In addition, the appearances of hobbyhorses and the occasional dragon or unicorn also hint at a pagan past, as these animals could be seen as a focus of worship. Outside of England in Brittany some small churches had a festival specially dedicated to the hobbyhorse, where the horse was adorned with flowers and paraded around the town. Though this was a supposedly Christian festival, it certainly seems more pagan to outside observers.
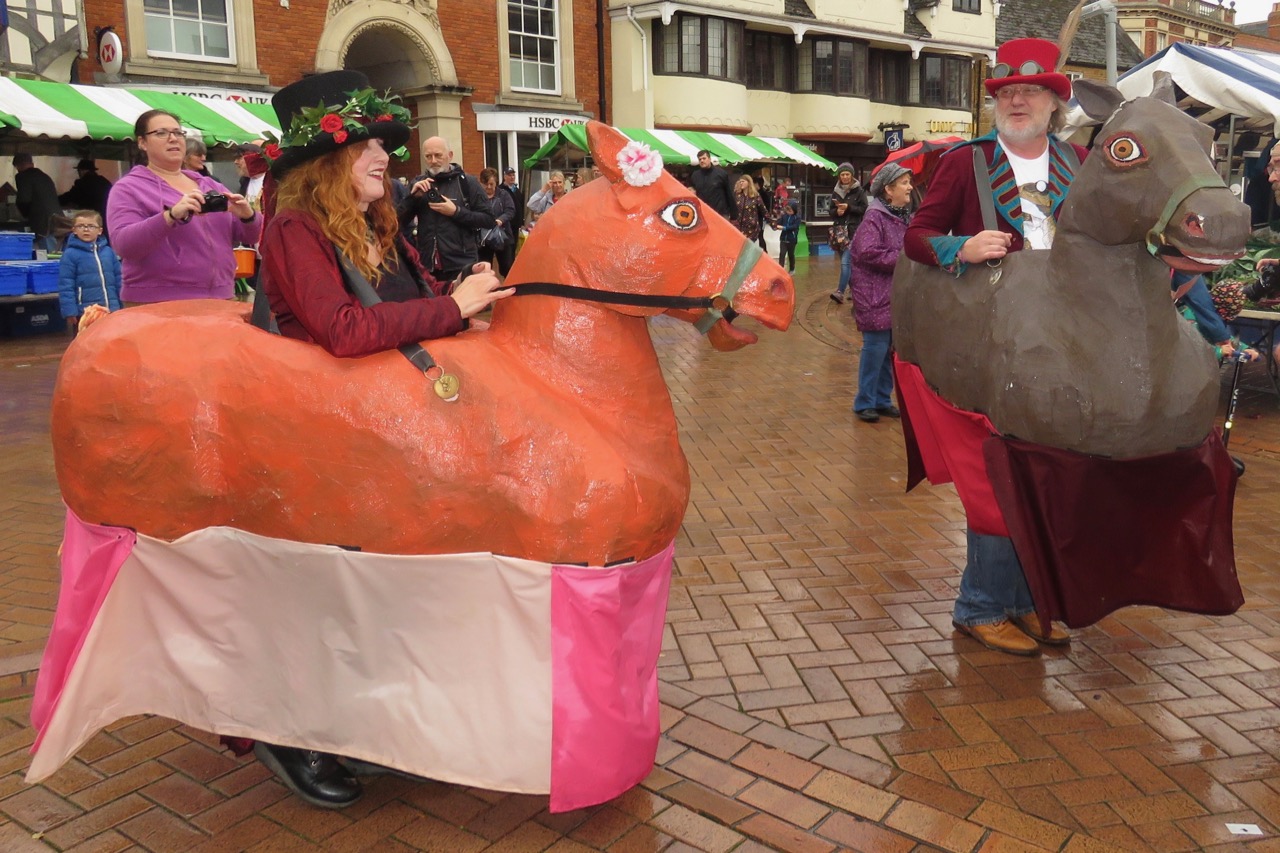 |
| Hobby Horses at the 2018 Banbury Folk and Hobby Horse Festival |
Opposed to dancing, drinking, and anything resembling a good time, Cromwell suppressed Morris dance into near extinction. However, the tradition survived. Morris dance resurfaced in the countryside after the restoration of the English monarchy. Morris dancing had fallen out of favor with the nobility, but it was adopted by the commoners. The common people couldn't afford the same elaborate costuming as the nobility, but they used ribbons, bells, flowers and colorful rags to add to their appearance. The modern Morris costume evolved from their imitations.
However, as Britain industrialized the dance began to fall out of style. Many young men moved to the factory towns, and were disinclined to continue Morris dancing. Early twentieth-century Morris dancers lamented that the younger generation was too proud to continue the tradition, because it was too much like begging. These young men might have changed their minds as time wore on, but unfortunately, many of those young men lost their lives in World War I.
Morris dance may have been lost to time had it not been carefully documented by the ethnochoreologist and ethnomusicologist Cecil Sharp. Sharp traveled England collecting folk dances and published several works on the subject. Sharp's books revived interest in Morris dance, and Morris began to be taught (and tested) in some English schools.
 |
Traditional sides are led by a Squire who arranges performances and is generally the man in charge. Under him is the Foreman or Captain who teaches the dances. Last on the leadership hierarchy is the Bagman, who serves as a secretary. Under them are the dancers, and the occasional Fool or Beast.
Beasts are Morris characters that add to the story of the dance. Common beasts are hobbyhorses, dragons, and unicorns. It can be difficult for Beasts to dance with the same nimbleness as the other dancers due to their cumbersome costume, but that doesn't stop many from trying. Hobbyhorses are the most common type of Beasts in modern practice.
There are six main styles of Morris dance still practiced in England today: Cotswold, Molly, Border, Northwest Clog, Longsword, and Rapper. While all are related, each style has a unique flavor and tradition.
Border
Quite possibly the oldest Morris tradition, Border Morris originated in the counties near the Welsh border, and, while simpler than Cotswold style, it is much more lively. It must be noted that, while it is sometimes called "Welsh Border Morris," Border Morris is an English dance and has little to do with Welsh folk dance traditions. Many border style dances have "fight sequences" choreographed into them. Historically these might have been done with actual swords, but they have been done with sticks or wooden swords since at least the 1800s.
Border Morris traditionally made an appearance in the winter, where men would dance for extra money when they couldn't farm or fish. This was considered a form of begging and was thus illegal, so dancers darkened their faces to avoid arrest. Dancers wore a rag coat, a tailcoat, women's clothing, or any other bits and bobs lying around. The main purpose of Border costume is to look eccentric. Border sides generally have a bigger band than other styles and are accompanied by a vigorous percussion section.
Border Morris traditionally made an appearance in the winter, where men would dance for extra money when they couldn't farm or fish. This was considered a form of begging and was thus illegal, so dancers darkened their faces to avoid arrest. Dancers wore a rag coat, a tailcoat, women's clothing, or any other bits and bobs lying around. The main purpose of Border costume is to look eccentric. Border sides generally have a bigger band than other styles and are accompanied by a vigorous percussion section.
Cotswold
The most commonly performed style, Cotswold Morris originated in the South Midlands, particularly the counties of Gloucestershire, Oxfordshire, Northamptonshire, and Warwickshire. Cotswold style survived the most intact after the Cromwell persecutions because of its location in the heart of royalist territory, and it was documented extensively by Cecil Sharp.
Cotswold dances are usually performed with six or eight dancers, and dancers generally wear white shirts with black or white pants. In addition to the dancers, there may also be a Fool, a Beast, or a cake impaled on a sword. Cotswold is notable for it's use of bells, or ruggles, attached beneath the knee of each dancer. Cotswold dancers may also wave handkerchiefs, bang sticks, or clap hands. Cotswold is traditionally performed around Whitsunday.
Cotswold dances are usually performed with six or eight dancers, and dancers generally wear white shirts with black or white pants. In addition to the dancers, there may also be a Fool, a Beast, or a cake impaled on a sword. Cotswold is notable for it's use of bells, or ruggles, attached beneath the knee of each dancer. Cotswold dancers may also wave handkerchiefs, bang sticks, or clap hands. Cotswold is traditionally performed around Whitsunday.
Longsword
Also called "hilt and point," Longsword Morris comes from Yorkshire, and is, as expected, danced with swords.³ Longsword dances are performed with six to eight dancers, with each dancer holding on to their own sword, as well as the end of their neighbor's sword to make a circle. Swords are, thankfully, blunt and around a meter long. During a Longsword dance, dancers weave between the swords, and end the dance by creating a star. Longsword, as well as the closely related Rapper, is most commonly performed during Christmas and New Year's.
Molly
Molly dance is unique in that it was less choreographed and organized than other types of Morris dance. Molly was traditionally performed as a part of the Plough Monday celebrations. Plough Monday, which takes place on the first Monday of January, was a day when ploughboys would drag a plough to the more affluent homes in the village and demand payment in money or food from the homeowners. If the ploughboys weren't satisfied with their payment, they would cut a long furrow through the homeowner's front lawn or doorstep.
Needless to say, Plough Monday was raucous at the best of times. Dancing accompanied the ceremonial shake-downs, and often random passersby would join in. Some male dancers would don women's clothing for the celebration, which gives the dance style its name ("Molly" being the contemporary pejorative for a man who wore women's clothing and male homosexuals). If not wearing petticoats, dancers wore whatever was closest to hand, and used black face paint to hide their identities--a necessity when committing property damage. Like most Morris dances, the origins of Molly are unclear, and there are no references to Molly dancing until the 1800s. Molly hasn't enjoyed the same revival as Border and Cotswold style, and traditional Plough Monday celebrations definitely aren't allowed anymore, but Molly dancing does accompany the "Straw Bear Festival" of Whittlesea, which occurs the weekend after Plough Monday.
Needless to say, Plough Monday was raucous at the best of times. Dancing accompanied the ceremonial shake-downs, and often random passersby would join in. Some male dancers would don women's clothing for the celebration, which gives the dance style its name ("Molly" being the contemporary pejorative for a man who wore women's clothing and male homosexuals). If not wearing petticoats, dancers wore whatever was closest to hand, and used black face paint to hide their identities--a necessity when committing property damage. Like most Morris dances, the origins of Molly are unclear, and there are no references to Molly dancing until the 1800s. Molly hasn't enjoyed the same revival as Border and Cotswold style, and traditional Plough Monday celebrations definitely aren't allowed anymore, but Molly dancing does accompany the "Straw Bear Festival" of Whittlesea, which occurs the weekend after Plough Monday.
Northwest Clog
Not to be confused with its Appalachian counterpart, Northwest Clog originated in the industrial towns of Cheshire, Lancashire, and West Yorkshire and came of age during the industrial revolution. As people from rural communities moved to manufacturing centers, they brought their Morris traditions with them, and a new dance tradition that imitated the machinery they worked with was formed.
Northwest Clog dances are danced in multiples of four, and traditionally the dancers wore colorful clothing, along with the heavy clogs they used in their factory work. Modern dancers wear clogs with iron taps on the toe and heel. Dancers also sometimes use sticks or slings and are led by a conductor, who uses a whistle to signal changes in the dance figure. Northwest Clog is traditionally performed during the annual rushbearing, which happens in the summertime.⁴
Northwest Clog dances are danced in multiples of four, and traditionally the dancers wore colorful clothing, along with the heavy clogs they used in their factory work. Modern dancers wear clogs with iron taps on the toe and heel. Dancers also sometimes use sticks or slings and are led by a conductor, who uses a whistle to signal changes in the dance figure. Northwest Clog is traditionally performed during the annual rushbearing, which happens in the summertime.⁴
Rapper
By far the most athletic of the Morris styles, Rapper dance hails from Durham and Northumberland. There are five dancers who are occasionally joined by the characters of Tom and Betty, who lead the dance. Dancers make use of "rappers," which are basically bendy swords with wooden handles on each end. This is the fastest of the Morris dances and, like Longsword, features dancers weaving between rappers and using their swords to create pictures. Rapper style also occasionally features backflips. Dancers wear hard-sole shoes and white shirts with black pants. Rapper dancers are traditionally performed during Christmas and New Year's.
It would be remiss of this historian to write about Morris dance but not talk about the live music that often accompanies the dancers. Morris bands utilize traditional instruments (concertina, fiddle, melodian, accordion, pipes, tabor) and are percussion driven. Bands can range in size from a single musician to tens of people, depending on the style of dance and the preference of the side. Musicians often dress to match the dancers and are an integral part of the performance.
Morris dancing, particularly Border Style and Molly Dance Morris, have met with controversy in recent years due to the fact that many Morris sides include black face paint as a part of their costume. The tradition of dancers blackening their faces has dozens of explanations dating from different eras, but some of the most common are:
 |
| Morris Men dressed in traditional Cotswold style costume. |
- Morris dancers in the Early Middle Ages blackened their faces because they were performing an ancient rite and needed to be disguised for this.
- Faces were blackened to imitate Moors during dances, which often told the tale of a Moorish vs. Christian battle.
- Dancers blackened their faces to hide their identities from the police because it was illegal to dance on public holidays.
- Morris dancing was often accompanied by a certain amount of criminal mischief, and dancers didn't want to be arrested.
- Morris dancers were shy. (No, seriously.)
- During the Industrial Revolution, many factory men had to supplement their income through dancing. They would wear face paint so their bosses didn't know about their side hustle.
- It's tradition, and face blackening helps the dancer get more into the dancing mood and feel less inhibited.
- It's a way of remembering the oppressive policies of the 1700s that disenfranchised the working class.
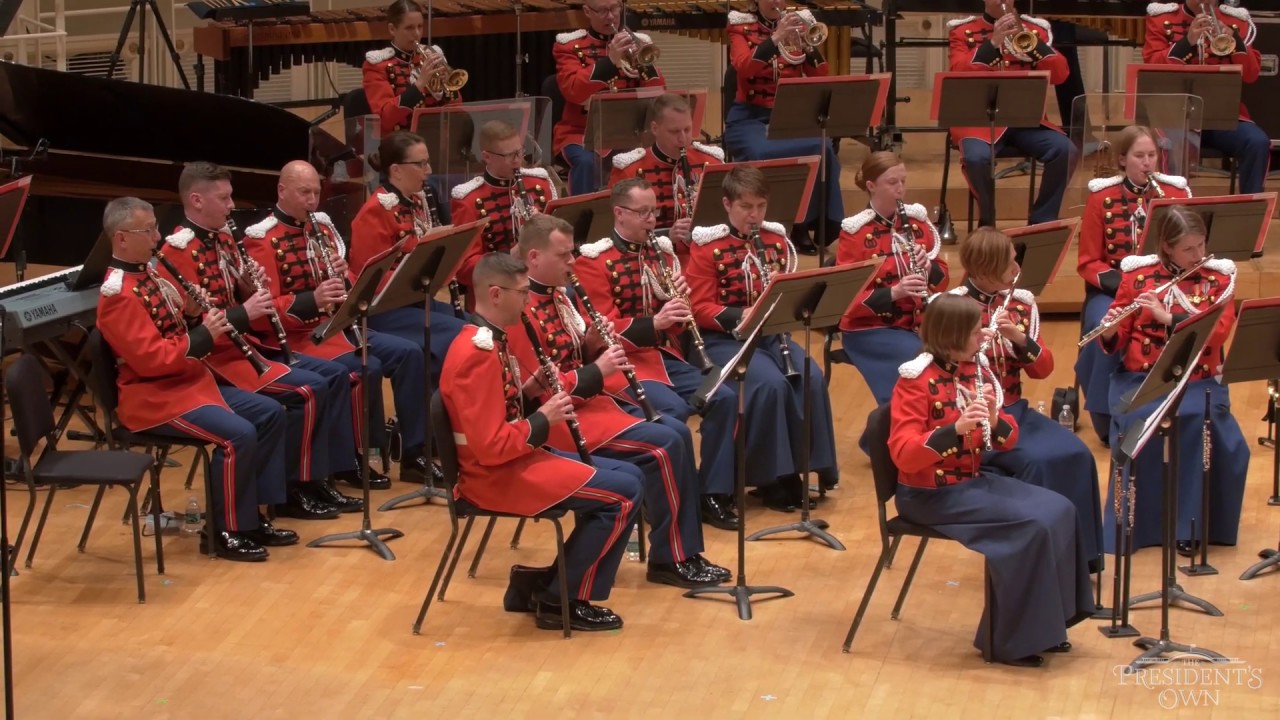 |
| Morris dance is also occasionally accompanied by a brass band or wind ensemble, but a traditional band is more popular. |
During its long history, Morris dance has transitioned from being an important pagan ritual, to being a way of making money, into a lighthearted celebration of English culture. Morris has evolved over the years, and undoubtedly will continue to do so, proving that culture and tradition are mutable.
¹One of the more colorful stories about Morris Dance from this era is that of the actor Will Kemp, who bet a friend that he could Morris dance from London to Norwich before the end of Lent. In a feat that would come to be known as his "Nine Day Wonder," Kemp danced the more than 100 miles between the two cities. While the entire journey took more than nine days, he did win his bet. While not the inspiration for, it is definitely reminiscent of Tony Hawks who, in the 1990s hitchhiked around the circumference of Ireland with a mini-fridge, also on a bet.
² The line was even thinner outside of England in Spain, where Morris dances often portrayed a battle between Christians and Muslims with the Christians emerging triumphant.
³Longsword Morris dance shouldn't be confused with Scottish Longsword dance, where the swords are placed on the ground.
⁴Unlike other Morris dances, Northwest Clog has always been a co-ed affair. Traditionally only men were allowed to Morris dance, but by the time Northwest Clog developed, this was no longer the case. While many Morris sides are mixed today, Northwest is the only style of Morris in which men and women dancing together has always been the norm.
This article was edited by Mara Kellogg.
⁴Unlike other Morris dances, Northwest Clog has always been a co-ed affair. Traditionally only men were allowed to Morris dance, but by the time Northwest Clog developed, this was no longer the case. While many Morris sides are mixed today, Northwest is the only style of Morris in which men and women dancing together has always been the norm.
This article was edited by Mara Kellogg.
Sources
"Morris and Morisca" by Violet Alford
"Some Other Hobby Horses" by Violet Alford
"Early Record of the Morris in England" by Lucile Armstrong and Barbara Lowe
"The Origins of the Morris Dance" by Rodney Gallop
"The Abram Morris Dance" by Maud Karpeles
"Some Notes on the Morris Dance" by Cecil J. Sharp
"The Earliest Reference to the Morris Dance?" by Michael Heaney
The Morris Tradition-Morris Ring
Molly Dancing-Morris Ring
Molly Dancing-Heritage Alive
Molly Dancing-Oxford Reference
Northwest Clog-Maldon Morris
Rapper Sword Dance-the Morris Ring
Longsword Dancing
Longsword-Mersey Morris Men
Morris Dancing From the Welsh Borders-Morris Ring
History of Border Morris and OBJ-OBJ
Beltane Border Morris
Morris Dancing From the Cotswolds-Morris Ring
A Brief History of Morris Dancing-Kettle Bridge Clogs
Cotswold Morris Dancers-Cotswolds Info
Morris Dance Music-Morris Ring
Molly Dancing-Morris Ring
Molly Dancing-Heritage Alive
Molly Dancing-Oxford Reference
Northwest Clog-Maldon Morris
Rapper Sword Dance-the Morris Ring
Longsword Dancing
Longsword-Mersey Morris Men
Morris Dancing From the Welsh Borders-Morris Ring
History of Border Morris and OBJ-OBJ
Beltane Border Morris
Morris Dancing From the Cotswolds-Morris Ring
A Brief History of Morris Dancing-Kettle Bridge Clogs
Cotswold Morris Dancers-Cotswolds Info
Morris Dance Music-Morris Ring