Though she's been largely forgotten to history, Sayyida al-Hurra--known as the 'Pirate Queen of Morocco'--ruled the entire west Mediterranean, as well as a sizable Moroccan city state in the 1500s. She harried the Spanish and Portuguese, invaded modern Gibraltar, and forced the smitten King of Morocco to marry her on her own terms. She was a remarkable woman, and we don't even know her name.
'Sayyida al-Hurra' is a title, not a name. It means 'noble lady who is free'. The title al-Hurra was given to women who ruled a kingdom (or queendom!) in their own right. For Sayyida, that kingdom was the coastal city state of Tétouan, where she ruled for a quarter of a century.
Sayyida was born in the then Muslim held Andalusia region of Spain. Her father, Moulay Ali ibn Rashid, was a tribal chief, and a wealthy man of Moroccan descent. However, they, along with many other Muslims, were forced out of Spain during the Reconquista. They fled south to Morocco, and with other refugee families, established the city of Chefchaouen. Sayyida's father was declared king, and as his daughter, Sayyida was given a good education, learning at least two languages and gaining an understanding of international diplomacy.
When she was sixteen Sayyida was married to the ruler of Tétouan. Though she was very young, her husband relied on her for political advice and support¹, and she soon became his chief wife. Tétouan had important trading connections with the Portuguese city of Ceuta, and Sayyida's language skills as well as her grasp of economics and diplomacy was an enormous asset to her husband.
Sayyida's husband died sometime between 1515 and 1519, and Sayyida was made the queen of Tétouan. As we've discussed before, it wasn't too unusual for a woman to be a regent to a young heir, or be a regent and then refuse to relinquish power, but in Sayyida's case she was named queen in her own right, and not a regent. According to Islamic historians, she was the last such queen to hold a city or region in her own right.²
At this time, thousands of refugees were still streaming in from Andalusia, and the Spanish and Portuguese were starting to sniff around Morocco. They were raiding, colonizing, and enslaving everyone and everywhere they could, and Sayyida, justifiably, had a massive beef with the Iberian's, so she decided to team up with the notorious pirate--Barbarossa.
With the help of Barbarossa, Sayyida assembled a fleet, and set about dominating the west Mediterranean. With Barbarossa controlling the east and Sayyida the west the pair gave the Spanish and Portuguese hell, invading and raiding all over the Iberian peninsula, seizing money, goods, and prisoners.
All of this raiding made Sayyida ridiculously wealthy, and extremely popular. In 1541 she caught the eye of Sultan Ahmed al-Wattasi, and he proposed. Sayyida accepted his proposal, but refused to leave her city, and marry in Fez. The fact that the Sultan acceded to her demand and married her in Tétouan is a testament to her strong will and the respect that Moroccans had for her.
However, Sayyida's power was waning. The Portuguese had had enough of her raiding, and the city of Ceuta cut off trade ties, putting many of Sayyida's people out of work. That combined with a coup led by her son-in-law led to Sayyida fleeing Tétouan in 1542. She returned to the city of her childhood--Chefchaouen--where she lived for another twenty years.
Today Sayyida is known as a great pirate queen, but there's more to her than that. She robbed and pillaged Spanish and Portuguese ships, but she also conducted refugees from Andalusia safely to Morocco. She used her network of pirates to protect her people from Iberian incursions into Morocco. The Moroccan's had no formal navy at the time, so Sayyida used her pirates to protect Morocco's coast This raises the question--was Sayyida a pirate or a protector?
¹This sort of thing was not uncommon. Andalusian Muslims had a strong tradition of women in leadership positions, and as such women's opinions and advice were respected and followed. This, however, does not nullify the fact that Sayyida was a remarkable leader.
²'al-Hurra' denotes a woman who is queen of a region in her own right.
Sources
Sayyida al Hurra
Lady Pirates: Queen of the Barbary Corsairs
Sayyida al-Hurra, Islamic Pirate Queen
Malika VI: Sayyida al-Hurra
 |
| Artists rendering of Sayida al-Hurra. There are no surviving portraits that are definitively of her. |
Sayyida was born in the then Muslim held Andalusia region of Spain. Her father, Moulay Ali ibn Rashid, was a tribal chief, and a wealthy man of Moroccan descent. However, they, along with many other Muslims, were forced out of Spain during the Reconquista. They fled south to Morocco, and with other refugee families, established the city of Chefchaouen. Sayyida's father was declared king, and as his daughter, Sayyida was given a good education, learning at least two languages and gaining an understanding of international diplomacy.
When she was sixteen Sayyida was married to the ruler of Tétouan. Though she was very young, her husband relied on her for political advice and support¹, and she soon became his chief wife. Tétouan had important trading connections with the Portuguese city of Ceuta, and Sayyida's language skills as well as her grasp of economics and diplomacy was an enormous asset to her husband.
Sayyida's husband died sometime between 1515 and 1519, and Sayyida was made the queen of Tétouan. As we've discussed before, it wasn't too unusual for a woman to be a regent to a young heir, or be a regent and then refuse to relinquish power, but in Sayyida's case she was named queen in her own right, and not a regent. According to Islamic historians, she was the last such queen to hold a city or region in her own right.²
| Modern Tétouan |
All of this raiding made Sayyida ridiculously wealthy, and extremely popular. In 1541 she caught the eye of Sultan Ahmed al-Wattasi, and he proposed. Sayyida accepted his proposal, but refused to leave her city, and marry in Fez. The fact that the Sultan acceded to her demand and married her in Tétouan is a testament to her strong will and the respect that Moroccans had for her.
However, Sayyida's power was waning. The Portuguese had had enough of her raiding, and the city of Ceuta cut off trade ties, putting many of Sayyida's people out of work. That combined with a coup led by her son-in-law led to Sayyida fleeing Tétouan in 1542. She returned to the city of her childhood--Chefchaouen--where she lived for another twenty years.
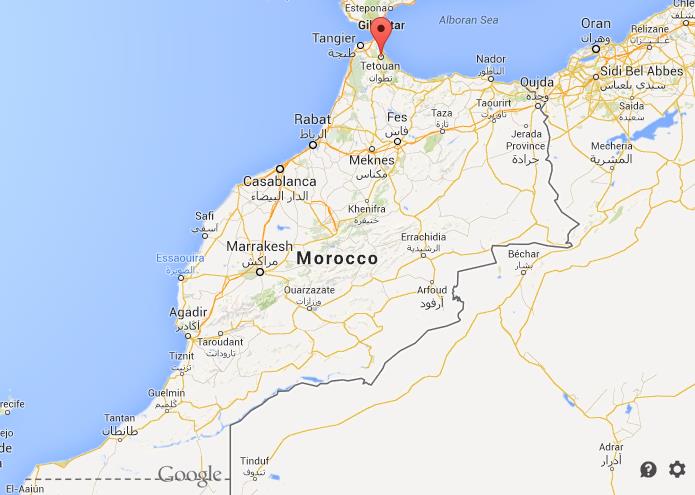 |
| Tétouan, Morocco |
¹This sort of thing was not uncommon. Andalusian Muslims had a strong tradition of women in leadership positions, and as such women's opinions and advice were respected and followed. This, however, does not nullify the fact that Sayyida was a remarkable leader.
²'al-Hurra' denotes a woman who is queen of a region in her own right.
Sources
Sayyida al Hurra
Lady Pirates: Queen of the Barbary Corsairs
Sayyida al-Hurra, Islamic Pirate Queen
Malika VI: Sayyida al-Hurra