Known among themselves as the Haudenosaunee,¹ the Iroquois League (or Confederacy) is the world's oldest participatory democracy. Located in what is today central New York state, the Haudenosaunee controlled vast swathes of woodland all the way into today's Ontario. A combination of six tribes, they banded together in mutual defense and adopted common policy in regards to other tribes and white settlers. Because of this cooperation, they were able to keep their territorial lands longer than any other confederacy in the region.
The Haudenosaunee is comprised of six individual tribes--the Oneida, Onondaga, Cayuga, Seneca, Mohawk, and Tuscarora. Their individual languages are related, and most are mutually intelligible to the others. It is this shared language family which initially brought the Haudenosaunee together. Additionally, linguistic evidence suggests that the Haudenosaunee are immigrants to the New England area. It is thought that the original five tribes--all but the Tuscarora--emigrated from the southern United States², and it is definitely known that the Tuscarora emigrated from North Carolina.
Originally, these six tribes were separate people, and warred with each other the same way in which the confederation later warred with non-confederation people. There were frequent raids on rival tribes, and an 'eye for an eye' philosophy prevailed. If a member from one tribe was killed, the family of that person would kill a member of the tribe that killed their family member, starting a never ending cycle of bloodshed. Among the Haudenosaunee, this epoch is known as 'The Dark Times'.
Enter Deganawida. Deganawida is a religious man, and has been told by the Great Spirit to make peace between the people. Problem was, Deganawida had a stutter, and needed a mouthpiece. To this end, he found Hiawatha. At the time, Hiawatha was a simple cannibal, doing his cannibal thing. However, one day while cooking his latest victim Hiawatha saw his reflection in his cooking pot, and realized that someone as beautiful as himself should not be eating people. While discarding of the corpse he no longer intended to eat, he met Deganawida, who named Hiawatha as his mouthpiece. Together Deganawida and Hiawatha set about uniting the five tribes--the Mohawk, Seneca, Cayuga, Onondaga, and Oneida.³
The Haudenosaunee confederacy was built upon a system of participatory democracy. Each tribe had one vote, and the chiefs of each clan,⁴ known as Sachems, helped each nation come to an agreement on how they would vote. The Confederacy established an inter-confederacy peace treaty, and a pact of mutual defense. Additionally, Confederacy members were able to move freely between the different nations. The Confederacy had very few laws, mostly focusing on foreign relations, but they immediately outlawed cannibalism. For any decision to be made on the behalf of the entire confederacy a unanimous vote had to be reached. Should complete agreement not be met, each tribe was free to proceed as they saw fit. This would eventually lead to the nations fighting on different sides during the American Revolution.
Together, the Haudenosaunee were a formidable foe. They regularly raided their Algonquin neighbors, and colonial settlements, gaining European goods despite having no formal trade agreements with white men. They also established a system of currency, based of of Wampum, and had a massive agricultural system, growing corn, beans, and squash.
When it came to colonial clashes, the Haudenosaunee preferred to remain neutral. During the French and Indian War many of the Haudenosaunee refused to take sides. They attempted to do the same during the American Revolution, but were unable. The Haudenosaunee saw the wars between the colonists as civil wars that were none of their business, but the English insisted that the Haudenosaunee honor their treaty of mutual defense with the English.
This divided the tribes into rival factions. Due to pressure from the English, most of the tribes sided with the English, but some tribes, most notably the Oneida and Tuscarora, sided with the Americans. This division nearly killed the confederacy, as tribes began to raid the villages of confederacy members. Despite this, the confederacy remained intact, if fragile, at the end of the Revolution.⁵
The Confederacy's form of government would become a major influence on the creation of the United States Constitution. Benjamin Franklin and Thomas Jefferson, both of whom were well acquainted with the Haudenosaunee, were inspired by the fact that each member nation had an equal say in the policy of the group.
Today the Haudenosaunee Confederacy is as strong as ever. They are recognized as their own nation, and have sent delegates to the United Nations, and issue their own passports.⁶ The nations have banded together multiple times in mutual defense when development and industrial projects threaten native lands, and lobby together for the return of cultural artifacts and human remains.
¹Meaning 'People of the Longhouse', based on the longhouses that the Haudenosaunee lived in. The name 'Iroquois' is a francosized version of the Algonquin word 'Irinakhoiw'. 'Iroquois' roughly translated, means 'real adders'. Like many colonial names for Native Americans, this is a pejorative. In this article I will refer to this group of people by the name they chose form themselves--Haudenosaunee.
²This conclusion was reached by comparison to other Native American languages. the Haudenosaunee languages are very closely related to the Cherokee language--a nation which originated in the southern United States. Additionally, non Haudenosaunee tribes in the New York area speak languages from the Algonquin group. This difference suggests that the Haudenosaunee were once related to, or acquainted with the Cherokee.
³The canny reader may be wondering about the Tuscarora. The Tuscarora Nation was added to the Haudenosaunee confederacy in the early 1700s when they were driven out of North Carolina by English Colonists.
⁴A tribe is comprised of a group of clans. Clans are matrilinial, and are headed by the eldest woman in each clan. There were eight major clans in the confederation, and intermarriage inside a clan was discouraged.
⁵Following the Revolution the young American government placed sanctions on all members of the confederacy, including the ones that supported them against the English. This united the confederacy against the Americans as they were forced off their lands and onto reservations in New York and Canada.
⁶Though the Iroquois passport was largely recognized in the United States traveling on an Iroquois passport after the events of September 11, 2001 became largely impossible. Additionally, many nations do not recognize Iroquois passports, and refuse entry to holders if they do not also have an American or Canadian passport.
Sources
Iroquois Confederacy- American Indian Confederation
Iroquois League: The Ancient and Powerful Union of Six Nations
Iroquois Confederacy
The League of the Iroquois
The Six Nations: Oldest Living Participatory Democracy on Earth
The Six Nations Confederacy During the American Revolution
 |
| The Haudenosaunee are known for having invented the sport of Lacrosse, and for being multiple time world champions. |
Originally, these six tribes were separate people, and warred with each other the same way in which the confederation later warred with non-confederation people. There were frequent raids on rival tribes, and an 'eye for an eye' philosophy prevailed. If a member from one tribe was killed, the family of that person would kill a member of the tribe that killed their family member, starting a never ending cycle of bloodshed. Among the Haudenosaunee, this epoch is known as 'The Dark Times'.
 |
| Map of Haudenosaunee lands |
The Haudenosaunee confederacy was built upon a system of participatory democracy. Each tribe had one vote, and the chiefs of each clan,⁴ known as Sachems, helped each nation come to an agreement on how they would vote. The Confederacy established an inter-confederacy peace treaty, and a pact of mutual defense. Additionally, Confederacy members were able to move freely between the different nations. The Confederacy had very few laws, mostly focusing on foreign relations, but they immediately outlawed cannibalism. For any decision to be made on the behalf of the entire confederacy a unanimous vote had to be reached. Should complete agreement not be met, each tribe was free to proceed as they saw fit. This would eventually lead to the nations fighting on different sides during the American Revolution.
Together, the Haudenosaunee were a formidable foe. They regularly raided their Algonquin neighbors, and colonial settlements, gaining European goods despite having no formal trade agreements with white men. They also established a system of currency, based of of Wampum, and had a massive agricultural system, growing corn, beans, and squash.
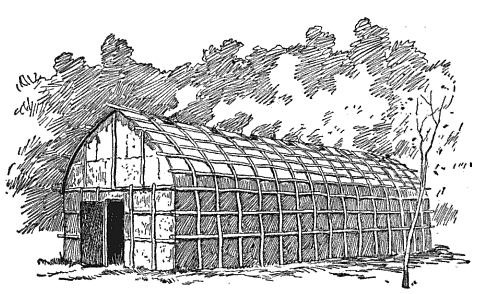 |
| The Haudenosaunee lived in Longhouses--wooden dwellings which housed multiple families. Longhouses could be anywhere between 50 to 150 feet long |
This divided the tribes into rival factions. Due to pressure from the English, most of the tribes sided with the English, but some tribes, most notably the Oneida and Tuscarora, sided with the Americans. This division nearly killed the confederacy, as tribes began to raid the villages of confederacy members. Despite this, the confederacy remained intact, if fragile, at the end of the Revolution.⁵
The Confederacy's form of government would become a major influence on the creation of the United States Constitution. Benjamin Franklin and Thomas Jefferson, both of whom were well acquainted with the Haudenosaunee, were inspired by the fact that each member nation had an equal say in the policy of the group.
 |
| Haudenosaunee Flag |
¹Meaning 'People of the Longhouse', based on the longhouses that the Haudenosaunee lived in. The name 'Iroquois' is a francosized version of the Algonquin word 'Irinakhoiw'. 'Iroquois' roughly translated, means 'real adders'. Like many colonial names for Native Americans, this is a pejorative. In this article I will refer to this group of people by the name they chose form themselves--Haudenosaunee.
 |
| Haudenosaunee passport |
³The canny reader may be wondering about the Tuscarora. The Tuscarora Nation was added to the Haudenosaunee confederacy in the early 1700s when they were driven out of North Carolina by English Colonists.
⁴A tribe is comprised of a group of clans. Clans are matrilinial, and are headed by the eldest woman in each clan. There were eight major clans in the confederation, and intermarriage inside a clan was discouraged.
⁵Following the Revolution the young American government placed sanctions on all members of the confederacy, including the ones that supported them against the English. This united the confederacy against the Americans as they were forced off their lands and onto reservations in New York and Canada.
⁶Though the Iroquois passport was largely recognized in the United States traveling on an Iroquois passport after the events of September 11, 2001 became largely impossible. Additionally, many nations do not recognize Iroquois passports, and refuse entry to holders if they do not also have an American or Canadian passport.
Sources
Iroquois Confederacy- American Indian Confederation
Iroquois League: The Ancient and Powerful Union of Six Nations
Iroquois Confederacy
The League of the Iroquois
The Six Nations: Oldest Living Participatory Democracy on Earth
The Six Nations Confederacy During the American Revolution