Though it came into existence before the start of the Cold War, Yugoslavia was a major communist player on the world stage during the 1900s. Officially and formally dissolving for good in 2006, Yugoslavia managed to last for nearly a century in some form or another.
Yugoslavia, as a country, had three distinct periods. Pre WWII Yugoslavia, Post WWII Yugoslavia, and Serbia-Montenegro Yugoslavia. However, when people talk about 'the former Yugoslavia', they are usually referring to the second incarnation--Post WWII Yugoslavia.
Today, the region that was once Yugoslavia is now the six¹ independent countries of North Macedonia, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Croatia, Slovenia, Serbia, and Montenegro. These countries have, ostensibly, very little in common. A mix of Catholic, Orthodox Christian, and Muslims, Yugoslavia wasn't even composed of a singular ethnic group--a fact that led to great tension during its (relatively) short time as a country.
The greatest unifying factor of the nations that became Yugoslavia was the fact that they were 1) Southern Slavic peoples² and 2) part of someone else's empire for hundreds of years. For years Serbia³, North Macedonia, and Montenegro were a part of the vast Ottoman Empire, and Croatia, Bosnia and Herzegovina,and Slovenia were a part of the Austro-Hungarian Empire. Though both Serbia and Montenegro had gained their independence at the time of WWI, the memories of former oppression was still strong.
It was these memories of oppression that ultimately brought these Southern Slav people together. Yugoslavian intellectuals believed that the only way to retain their freedoms and ethnic identities was to band together and protect each other from everyone else. In order to realize this idea the 'Kingdom of Serbs, Croats, and Slovenes' was created in 1918.
This first reincarnation of Yugoslavia went about as well as could be expected. Multiple ethnic groups with their own interests unified only by a general shared ancestry couldn't really be expected to get along well. Throw in a large minority of Albanians who really didn't want to be there, and you have a recipe for disaster. The young state was plagued with infighting and violence until it was invaded by Third Reich Germany in 1941.
As in most cases, when faced with a common enemy, the Yugoslavs managed to band together, and take out the Germans. By the end of WWII Yugoslavia was ready to go again, this time as the Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia.
In 1946 Josip Broz Tito, the Croat leader of the Yugoslav army, liberated Yugoslavia from Germany, and was installed as president. Tito was a great admirer of Stalin, and wanted to create a communist state in Yugoslavia. Basing his system on the same system used in the USSR, Tito formed a centralized government, with all six member countries having an equal say in governing. However, many constitutional changes led Yugoslavia to become a loose confederation of states largely run by independent companies working on the government's behalf.
This wasn't very communist, and Stalin didn't care for it. However, Tito, who had been declared president for life, didn't really care what Stalin thought, and divorced himself and Yugoslavia from the USSR. Though a communist country, Yugoslavia allowed tourism to, and from, the west. They experienced a post war economic boom, and the north and west of Yugoslavia did very well financially.
However, Yugoslav prosperity was built on a series of loans from the International Monetary Fund (IMF) and other countries. Following Tito's death in 1980, leadership of Yugoslavia was delegated to a rotating set of representatives from each country, and the IMF demanded a restructuring of the Yugoslavian economic system. That, in addition to internal violence, lead Slovenia to declare independence in 1991.
Following Slovenia's departure, Croatia, Bosnia and Herzegovina, and North Macedonia were close behind. Only Serbia and Montenegro remained, and they banded together to become the third Yugoslavia.
However, the third Yugoslavia, now just known as Serbia and Montenegro, wasn't to last long either, in 2006 the union disbanded, breaking up Yugoslavia for good.
There's many reasons why Yugoslavia is no longer on the map, but the major reason is the lack of a stable leadership system. Josip Tito was president for nearly 40 years, and it was his leadership that largely kept Yugoslavia together. Lack of a workable system for deciding executive leadership after his death is what lead to the breakdown of the Yugoslav economy and unity.
Though seemingly innocuous, Yugoslavia played a major part in the Cold War. Tito was the first communist leader to defy Stalin, and his refusal to bow to the USSR or the US made Yugoslavia the first non-aligned state. As a non-aligned state, Yugoslavia was able to concentrate on its own interests instead of playing the communist vs. capitalist game for the last half of the 20th century.
¹Seven if you consider Kosovo to be its own country
²'Yugoslavia' means 'Land of the Southern Slavs'
³Serbia was actually part of both the Ottoman and the Austro-Hungarian Empires at one point in their history. Additionally, Serbia gained its independence from the Ottomans in 1878. Serbia then spent the next three decades being a major trouble maker on the Austro-Hungarian border until a Serbian shot Archduke Ferdinand in 1914, starting WWI
Article updated in 2019 to reflect the name change of North Macedonia. Northern Macedonia was known as "Former Yugoslav Republic of Macedonia" until February of 2019.
Sources
Yugoslavia-Encyclopedia Britannica
The Breakup of Yugoslavia: 1990-1992
Yugoslavia: 1918-2003
What is the Former Yugoslavia
Yugoslavia-Holocaust Encyclopedia
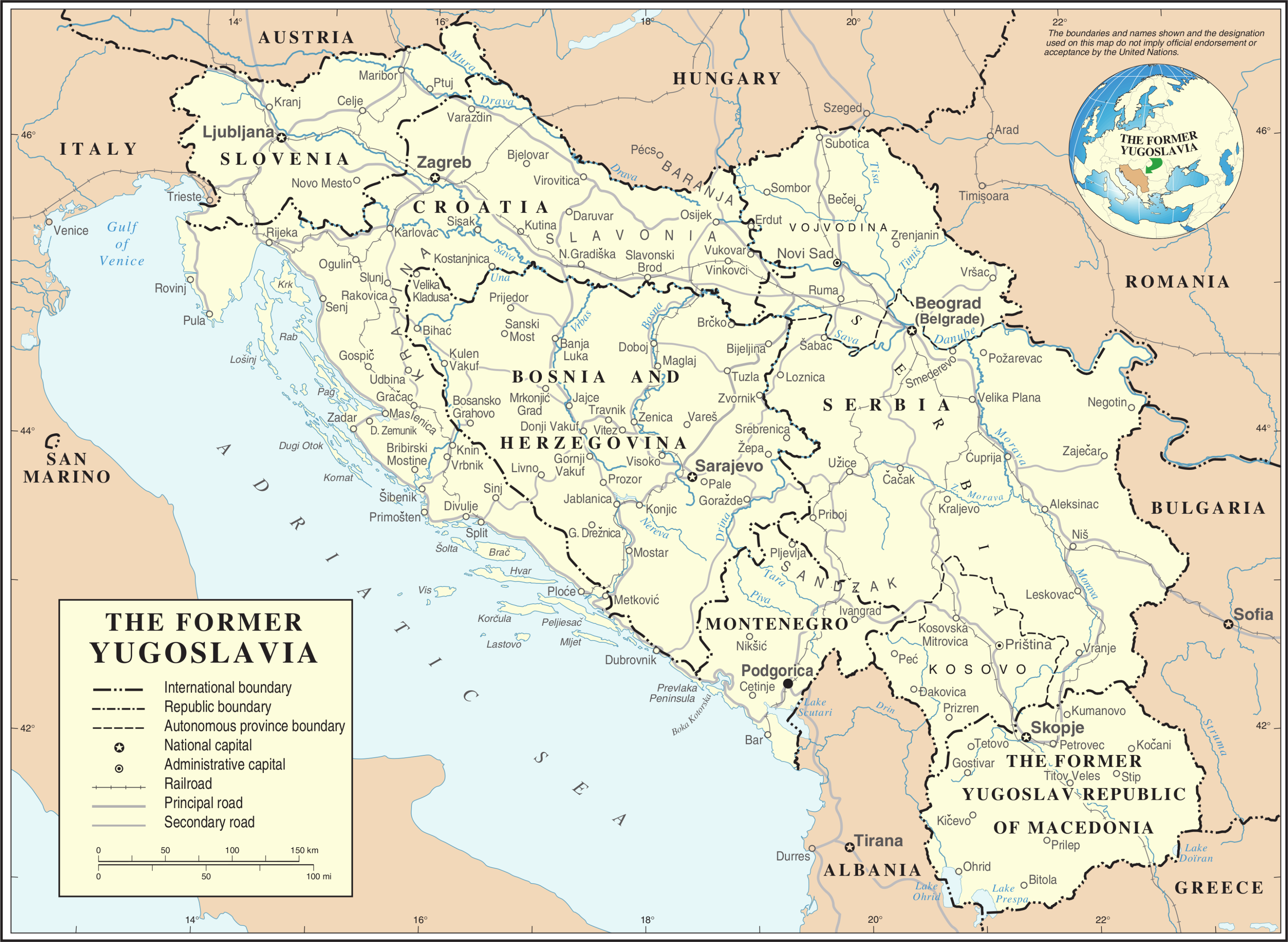 |
| Yugoslavia at its height. |
Today, the region that was once Yugoslavia is now the six¹ independent countries of North Macedonia, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Croatia, Slovenia, Serbia, and Montenegro. These countries have, ostensibly, very little in common. A mix of Catholic, Orthodox Christian, and Muslims, Yugoslavia wasn't even composed of a singular ethnic group--a fact that led to great tension during its (relatively) short time as a country.
The greatest unifying factor of the nations that became Yugoslavia was the fact that they were 1) Southern Slavic peoples² and 2) part of someone else's empire for hundreds of years. For years Serbia³, North Macedonia, and Montenegro were a part of the vast Ottoman Empire, and Croatia, Bosnia and Herzegovina,and Slovenia were a part of the Austro-Hungarian Empire. Though both Serbia and Montenegro had gained their independence at the time of WWI, the memories of former oppression was still strong.
It was these memories of oppression that ultimately brought these Southern Slav people together. Yugoslavian intellectuals believed that the only way to retain their freedoms and ethnic identities was to band together and protect each other from everyone else. In order to realize this idea the 'Kingdom of Serbs, Croats, and Slovenes' was created in 1918.
This first reincarnation of Yugoslavia went about as well as could be expected. Multiple ethnic groups with their own interests unified only by a general shared ancestry couldn't really be expected to get along well. Throw in a large minority of Albanians who really didn't want to be there, and you have a recipe for disaster. The young state was plagued with infighting and violence until it was invaded by Third Reich Germany in 1941.
As in most cases, when faced with a common enemy, the Yugoslavs managed to band together, and take out the Germans. By the end of WWII Yugoslavia was ready to go again, this time as the Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia.
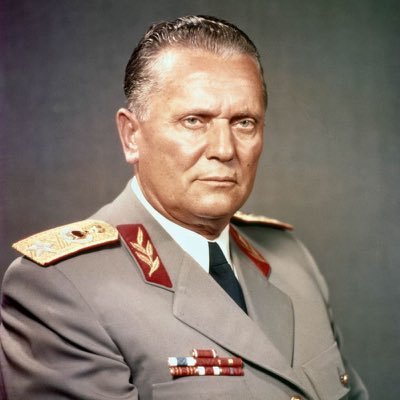 |
| Josip Broz Tito, Leader of Yugoslavia from 1946-1980 |
This wasn't very communist, and Stalin didn't care for it. However, Tito, who had been declared president for life, didn't really care what Stalin thought, and divorced himself and Yugoslavia from the USSR. Though a communist country, Yugoslavia allowed tourism to, and from, the west. They experienced a post war economic boom, and the north and west of Yugoslavia did very well financially.
However, Yugoslav prosperity was built on a series of loans from the International Monetary Fund (IMF) and other countries. Following Tito's death in 1980, leadership of Yugoslavia was delegated to a rotating set of representatives from each country, and the IMF demanded a restructuring of the Yugoslavian economic system. That, in addition to internal violence, lead Slovenia to declare independence in 1991.
Following Slovenia's departure, Croatia, Bosnia and Herzegovina, and North Macedonia were close behind. Only Serbia and Montenegro remained, and they banded together to become the third Yugoslavia.
However, the third Yugoslavia, now just known as Serbia and Montenegro, wasn't to last long either, in 2006 the union disbanded, breaking up Yugoslavia for good.
 |
| Yugoslavia flag |
¹Seven if you consider Kosovo to be its own country
²'Yugoslavia' means 'Land of the Southern Slavs'
³Serbia was actually part of both the Ottoman and the Austro-Hungarian Empires at one point in their history. Additionally, Serbia gained its independence from the Ottomans in 1878. Serbia then spent the next three decades being a major trouble maker on the Austro-Hungarian border until a Serbian shot Archduke Ferdinand in 1914, starting WWI
Article updated in 2019 to reflect the name change of North Macedonia. Northern Macedonia was known as "Former Yugoslav Republic of Macedonia" until February of 2019.
Sources
Yugoslavia-Encyclopedia Britannica
The Breakup of Yugoslavia: 1990-1992
Yugoslavia: 1918-2003
What is the Former Yugoslavia
Yugoslavia-Holocaust Encyclopedia